Want to maximize muscle building but confused about which foods actually matter? Here’s the science-backed list of the most effective muscle-building foods.
You’re training hard. Lifting heavy. Following progressive overload.
But your muscle growth has stalled.
You know nutrition matters, but with so much conflicting information, you’re not sure which foods actually build muscle and which are just hyped by influencers.
Some people swear by chicken and rice. Others claim you need exotic superfoods. Everyone has a different opinion.
Here’s the truth that will simplify your nutrition: The best foods for muscle building share common characteristics: high protein quality, appropriate calorie density, nutrient density, cost-effectiveness, and practicality. While no single food is mandatory, strategic food choices make hitting your macros easier and support better results. This list provides options to build a sustainable muscle-building diet, not a restrictive rulebook.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll reveal the 20 most effective muscle-building foods with scientific reasoning, explain the key characteristics that make certain foods superior for muscle growth, show you how to incorporate these foods into practical meal plans, provide budget-friendly alternatives when expensive options don’t fit your situation, and help you understand that variety matters more than perfection.
Whether you’re bulking, cutting, or maintaining, this article will optimize your food choices.
Let’s build your muscle-building nutrition foundation.
Understanding What Makes a Food “Good” for Muscle Building
Before examining specific foods, understand the criteria.
Characteristic 1: High-Quality Protein
The most important factor for muscle building foods.
What “high-quality protein” means:
Complete amino acid profile:
- Contains all nine essential amino acids
- Body cannot produce these
- Must come from diet
- Critical for muscle protein synthesis
High leucine content:
- Leucine triggers mTOR pathway
- Activates muscle-building processes
- 2-3g per meal optimal
- Found abundantly in animal proteins
High biological value:
- Measure of protein utilization
- Higher = better muscle building
- Animal proteins typically higher
- Some plant proteins also excellent
Examples:
- Eggs: 100 biological value
- Whey protein: 104 biological value
- Chicken: 79 biological value
- Soy protein: 74 biological value
Characteristic 2: Appropriate Calorie Density
Different goals require different calorie densities.
For bulking (muscle gain):
Need calorie-dense foods:
- Easy to create surplus
- Don’t fill you up too much
- Allow eating enough total calories
- Examples: Nuts, oils, rice, pasta
For cutting (fat loss while preserving muscle):
Need lower calorie density:
- High volume, low calories
- Keep you full on deficit
- Support satiety
- Examples: Lean meats, vegetables, egg whites
The balance:
- Choose foods matching your current goal
- Bulking: Include more calorie-dense options
- Cutting: Emphasize volume and satiety
- Both: Ensure adequate protein
Characteristic 3: Micronutrient Density
Vitamins and minerals support muscle building indirectly.
Important micronutrients for muscle growth:
Iron:
- Oxygen transport to muscles
- Energy production
- Performance support
- Found in: Red meat, lentils, spinach
Zinc:
- Testosterone production
- Protein synthesis
- Immune function
- Found in: Beef, oysters, pumpkin seeds
Magnesium:
- Muscle contraction
- Energy production
- Recovery
- Found in: Nuts, whole grains, dark chocolate
Vitamin D:
- Testosterone support
- Calcium absorption
- Immune function
- Found in: Fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified milk
B-vitamins:
- Energy metabolism
- Protein synthesis
- Recovery
- Found in: Meat, eggs, whole grains
Characteristic 4: Cost-Effectiveness
Building muscle is a long-term process. Nutrition must be affordable.
Best value protein sources:
- Eggs: ~$0.15-0.25 per 6g protein
- Chicken breast: ~$0.40-0.60 per 25g protein
- Canned tuna: ~$0.50-0.75 per 20g protein
- Greek yogurt: ~$0.60-1.00 per 15g protein
Expensive but not necessarily better:
- Grass-fed beef: 3x cost of regular beef, minimal difference
- Organic chicken: 2x cost, similar protein quality
- Exotic protein powders: Often unnecessary
The reality: Build your diet foundation on affordable, high-quality foods. Expensive options are optional luxuries, not necessities.
Characteristic 5: Practicality and Versatility
The best foods are ones you’ll actually eat consistently.
Practical considerations:
Preparation time:
- Eggs: 5 minutes
- Chicken breast: 20-30 minutes
- Canned tuna: 0 minutes
- Complexity affects adherence
Storage:
- Rice: Shelf-stable months
- Fresh fish: 1-2 days refrigerated
- Canned foods: Years
- Easier storage = better adherence
Portability:
- Nuts: Extremely portable
- Greek yogurt: Moderately portable
- Cooked chicken: Requires container
- Affects convenience
Versatility:
- Eggs: Dozens of preparation methods
- Rice: Pairs with everything
- Single-use foods: Limited applications
- Variety prevents boredom

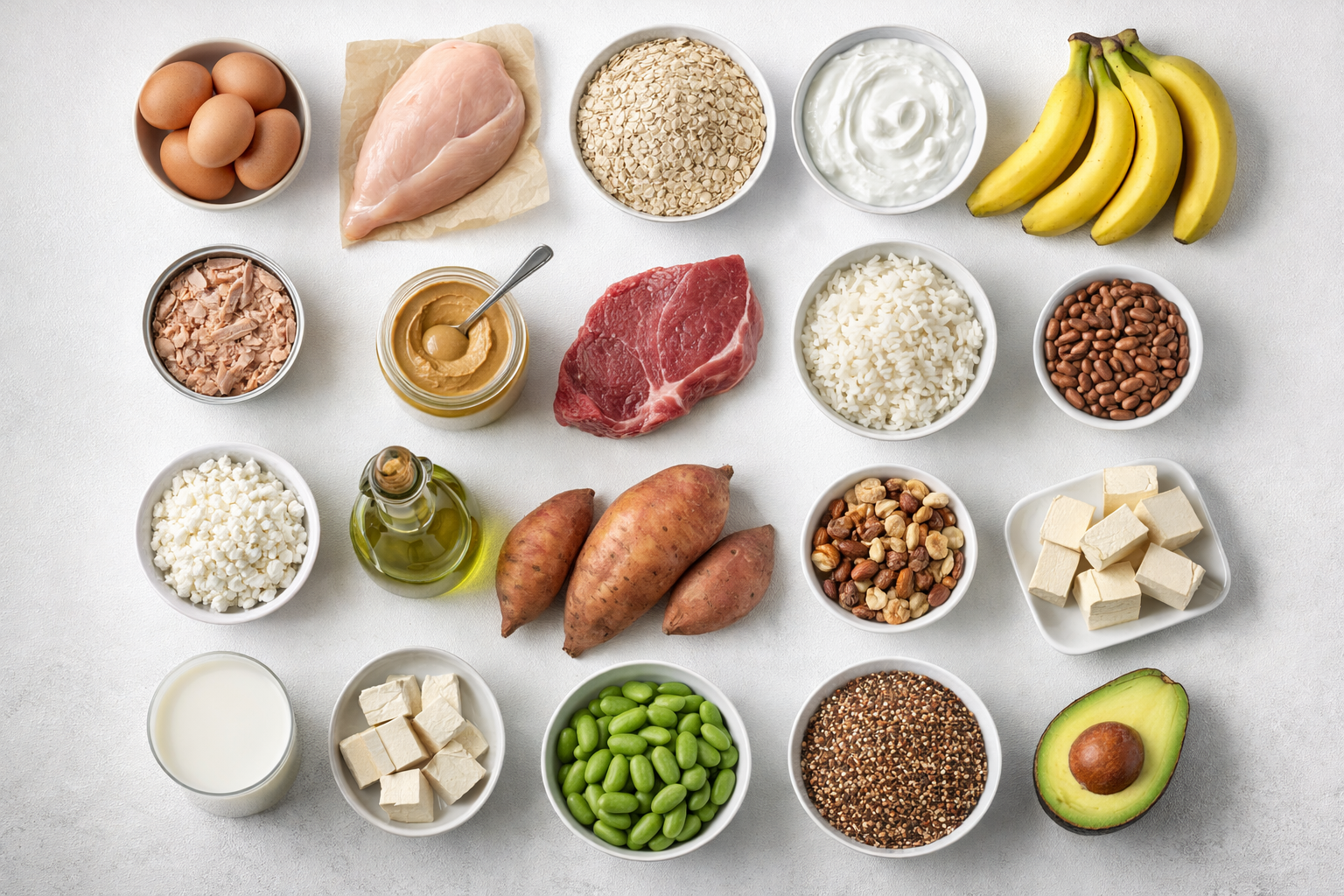
The 20 Best Foods for Muscle Building
Evidence-based food selections with practical reasoning.
1. Whole Eggs
Why they’re exceptional:
Complete protein powerhouse:
- 6g protein per large egg
- All essential amino acids
- High biological value (100)
- One of nature’s perfect proteins
Nutrient density:
- Vitamin D (bone health, testosterone)
- Choline (brain function, muscle signaling)
- Healthy fats (hormone production)
- Omega-3s (inflammation reduction)
Practical benefits:
- Extremely affordable ($0.15-0.25 per egg)
- Fast to prepare (5-10 minutes)
- Incredibly versatile (scrambled, boiled, omelet, baked)
- Long shelf life
How to use:
- Breakfast: 3-4 whole eggs scrambled
- Snack: Hard-boiled eggs
- Addition: Add to rice bowls or salads
- Target: 2-4 eggs daily
Don’t fear the yolks: Most nutrients are in the yolk. Whole eggs are superior to egg whites for muscle building.
2. Chicken Breast
The bodybuilding staple for good reason.
Protein efficiency:
- 31g protein per 4oz serving
- Minimal fat (3-4g per 4oz)
- Very lean (ideal for cutting)
- Complete amino acid profile
Cost-effectiveness:
- One of cheapest protein sources per gram
- Usually $3-5 per pound
- Provides 100g+ protein per pound
- Excellent value
Practical advantages:
- Batch cooking friendly (meal prep)
- Pairs with everything
- Neutral flavor (takes seasoning well)
- Available everywhere
How to use:
- Meal prep: Bake 3-5 pounds Sunday
- Lunch/dinner: 6-8oz per meal
- Versatile: Season differently for variety
- Target: 8-12oz daily when bulking
3. Oats
The muscle-building carbohydrate foundation.
Why oats excel:
Quality carbohydrate source:
- 27g carbs per 1/2 cup dry
- Complex carbs (sustained energy)
- 4g fiber (digestive health)
- 5g protein (bonus)
Muscle-building support:
- Provides energy for training
- Supports glycogen replenishment
- Easy to digest
- Doesn’t cause bloating for most
Incredible versatility:
- Oatmeal bowls (sweet or savory)
- Protein shakes (blended)
- Pancakes (oat flour)
- Baked goods (cookies, muffins)
How to use:
- Breakfast: 1 cup oats + protein powder + banana
- Shakes: 1/2 cup in mass gainer shake
- Snacks: Protein oatmeal cookies
- Target: 1-2 cups daily when bulking
4. Greek Yogurt
Protein-packed dairy excellence.
Protein content:
- 15-20g protein per cup
- Combination of whey and casein
- Complete amino acids
- High leucine content
Additional benefits:
- Probiotics (gut health)
- Calcium (bone health, muscle contraction)
- Versatile texture
- Satisfying and filling
Practical use:
- Quick protein source (no cooking)
- Portable (take to work)
- Mixes well (smoothies, parfaits)
- Multiple fat percentages (full-fat for bulking, non-fat for cutting)
How to use:
- Breakfast: 1-2 cups + granola + berries
- Snack: Plain with fruit
- Dessert: Mixed with protein powder
- Target: 1-2 cups daily
Choose plain, unsweetened: Flavored versions have 15-25g added sugar.
5. Bananas
The perfect portable carbohydrate.
Why bananas matter:
Quick energy source:
- 27g carbs per medium banana
- Fast-digesting (good pre/post workout)
- Natural sugars for glycogen
- Potassium (muscle function, cramping prevention)
Unmatched convenience:
- Pre-packaged by nature
- No refrigeration needed
- Eat anywhere
- No preparation required
Versatility:
- Eat alone
- Add to oatmeal or yogurt
- Blend in shakes
- Bake in recipes
How to use:
- Pre-workout: 1 banana 60-90 min before training
- Post-workout: 1-2 bananas in shake
- Snacks: Quick carb source
- Target: 2-4 daily when bulking
6. Canned Tuna
Budget-friendly protein convenience.
Protein efficiency:
- 20-25g protein per can
- Minimal fat (if in water, not oil)
- Very affordable ($0.50-1.00 per can)
- Complete amino acids
Omega-3 content:
- Supports anti-inflammation
- Heart health
- Recovery enhancement
- Joint health
Practical advantages:
- No cooking required
- Shelf-stable (years)
- Extremely portable
- Quick protein hit
How to use:
- Lunch: Tuna + rice + vegetables
- Snack: Tuna on rice cakes
- Salad: Mixed greens + tuna
- Target: 1-2 cans daily (be mindful of mercury, limit to 3-4 cans weekly)
Choose “in water” not “in oil”: Save calories for more food.
7. Natural Peanut Butter
Calorie-dense muscle-building staple.
Calorie density:
- 190 calories per 2 tablespoons
- 8g protein
- 16g healthy fats
- Easy to add calories when bulking
Additional benefits:
- Vitamin E (antioxidant)
- Magnesium (muscle function)
- Delicious (adherence factor)
- Versatile
How to use:
- Shakes: 2-4 tablespoons in mass gainer
- Snacks: Apples or bananas with PB
- Meals: Mixed into oatmeal
- Target: 2-4 tablespoons daily when bulking
Choose natural: Ingredients should be just peanuts (maybe salt). Avoid added sugar and hydrogenated oils.
8. Lean Red Meat
Nutrient-dense protein with unique benefits.
Protein and nutrients:
- 25-30g protein per 4oz
- Complete amino acids
- Highly bioavailable
- Excellent protein quality
Unique micronutrients:
- Heme iron (best absorbed form)
- Zinc (testosterone support)
- Creatine (performance, naturally occurring)
- B-vitamins (energy metabolism)
Lean cuts to choose:
- Sirloin
- Round (top, bottom, eye)
- Flank steak
- 93/7 or 96/4 ground beef
How to use:
- Dinner: 6-8oz lean steak
- Ground beef: Tacos, pasta sauce, rice bowls
- Meal prep: Batch cook for week
- Target: 8-12oz 2-3 times weekly
Not necessary daily: 2-3 times weekly provides benefits without excess.
9. White Rice
The muscle-building carbohydrate champion.
Why white rice is superior for bulking:
Easy to digest:
- Low fiber (easier to eat large amounts)
- Doesn’t cause bloating
- Gentle on stomach
- Supports high volume eating
Affordable and accessible:
- One of cheapest carb sources
- Available everywhere
- Long shelf life
- Simple preparation
Versatile:
- Pairs with any protein
- Takes any seasoning
- Multiple preparation methods
- Never gets old
How to use:
- Lunch/dinner: 1.5-2 cups cooked with protein
- Meal prep: Cook large batch Sunday
- Bulking: Can eat 3-4 cups daily easily
- Target: 2-4 cups cooked daily when bulking
White vs. brown rice: For muscle building, white is better (easier to eat more, similar results).
10. Beans
Underrated muscle-building food.
Macro combination:
- 15g protein per cup (plant-based)
- 40g carbs
- 12g fiber
- Complete nutrition package
Micronutrient density:
- Iron
- Magnesium
- Folate
- Potassium
Budget-friendly:
- One of cheapest protein sources
- Dried beans extremely affordable
- Canned convenient
- Excellent value
How to use:
- Side dish: Black beans with rice
- Meals: Bean bowls, chili, soups
- Salads: Mixed beans
- Target: 1-2 cups daily
Why bodybuilders skip beans: Mostly convenience/gas issues, not because they’re ineffective.

11. Extra Virgin Olive Oil
Healthy fat for muscle-building calories.
Calorie density:
- 120 calories per tablespoon
- Pure healthy fat
- Easy way to add calories
- Supports hormone production
Health benefits:
- Monounsaturated fats
- Anti-inflammatory
- Heart health
- Testosterone support
How to use:
- Cooking: Sauté vegetables, meat
- Drizzle: Over rice, pasta, salads
- Hidden calories: Add to shakes (yes, really)
- Target: 2-4 tablespoons daily when bulking
Buy quality: Look for “extra virgin” and darker bottles (protects from light damage).
12. Sweet Potato
Nutrient-dense carbohydrate source.
Nutritional profile:
- 25g carbs per medium potato
- 4g fiber
- Vitamin A (immune function, vision)
- Potassium (muscle function)
Practical benefits:
- Affordable
- Easy to prepare (bake, microwave, boil)
- Naturally sweet (satisfying)
- Versatile
How to use:
- Pre-workout meal: 8oz 2-3 hours before training
- Post-workout: With protein
- Meal prep: Bake multiple at once
- Target: 8-16oz daily when bulking
13. Nuts (Almonds, Walnuts, Cashews)
Calorie-dense nutrient powerhouses.
Nutritional benefits:
- 160-200 calories per ounce
- 5-7g protein per ounce
- Healthy fats
- Vitamin E, magnesium, zinc
Practical advantages:
- Zero preparation needed
- Extremely portable
- Long shelf life
- Instant snack
How to use:
- Snacks: 1-2oz between meals
- Addition: Sprinkle on yogurt, oatmeal
- Travel: Perfect on-the-go food
- Target: 1-3oz daily when bulking
Don’t overdo it: Very easy to eat 500+ calories without realizing.
14. Cottage Cheese
High-protein dairy option.
Protein content:
- 12-14g protein per 1/2 cup
- Mostly casein (slow-digesting)
- Complete amino acids
- Excellent before bed
Low calorie (if choosing low-fat):
- 1% cottage cheese: 80 calories per 1/2 cup
- Perfect for cutting
- High protein, low everything else
How to use:
- Snack: With fruit
- Before bed: Slow-release protein overnight
- Breakfast: Mixed with berries
- Target: 1-2 cups daily
15. Milk
Complete nutrition in liquid form.
Protein and more:
- 8g protein per cup
- Combination whey and casein
- Calcium, vitamin D
- Affordable
Calorie flexibility:
- Skim: 80 cal per cup (cutting)
- Whole: 150 cal per cup (bulking)
- Adjust to goals
How to use:
- Shakes: Liquid base for protein shakes
- Cereal/oatmeal: Instead of water
- Drinking: With meals
- Target: 2-4 cups daily
If lactose intolerant: Lactose-free milk or plant alternatives (soy, oat).
16. Tofu
Plant-based protein option.
Protein content:
- 10g protein per 1/2 cup
- Complete amino acids (rare for plant protein)
- Low calorie
- Versatile texture
Additional benefits:
- Soy protein quality
- Iron, calcium
- Takes any flavor
- Affordable
How to use:
- Stir fry: With vegetables and rice
- Scrambled: Tofu scramble breakfast
- Grilled: Marinated and baked
- Target: 1-2 servings daily (if plant-based)
17. Avocado
Healthy fat and micronutrients.
Calorie density:
- 240 calories per whole avocado
- 20g healthy fats
- Easy calories when bulking
- Nutrient-dense
Micronutrients:
- Potassium (more than bananas)
- Vitamin E
- B-vitamins
- Fiber
How to use:
- Addition: To meals, sandwiches, salads
- Snack: Half avocado alone
- Breakfast: Avocado toast with eggs
- Target: 1/2 to 1 whole daily when bulking
18. Lentils
Protein and carbs combined.
Nutritional profile:
- 18g protein per cup cooked
- 40g carbs
- 16g fiber
- Iron, folate
Budget superstar:
- One of cheapest protein sources
- Dried lentils incredibly affordable
- Complete meal base
- Excellent value
How to use:
- Soups: Lentil soup
- Bowls: Lentil and rice bowls
- Salads: Mixed in
- Target: 1-2 cups 2-3 times weekly
19. Edamame
Plant-based protein snack.
Protein quality:
- 17g protein per cup
- Complete amino acids
- Soy protein
- Quick preparation
How to use:
- Snack: Steamed with salt
- Addition: To salads, stir fries
- Portable: Take to work
- Target: 1-2 cups 2-3 times weekly
20. Quinoa
Complete plant protein grain.
Unique benefits:
- 8g protein per cup cooked
- All essential amino acids
- Complex carbs
- Gluten-free
How to use:
- Instead of rice: Meal base
- Bowls: Buddha bowls, grain bowls
- Salads: Quinoa salad
- Target: 1-2 cups 2-3 times weekly

How to Build Meals From These Foods
Practical meal construction.
Bulking Meal Examples
Meal 1: Power Breakfast
- 4 whole eggs (24g protein)
- 1.5 cups oats (10g protein)
- 1 banana (27g carbs)
- 2 tbsp peanut butter (8g protein, 190 cal)
- Total: ~42g protein, 850 calories
Meal 2: Classic Lunch
- 8oz chicken breast (62g protein)
- 2 cups white rice (90g carbs)
- 1 cup broccoli (fiber, micronutrients)
- 1 tbsp olive oil (120 cal)
- Total: ~62g protein, 750 calories
Meal 3: Muscle-Building Dinner
- 8oz lean beef (60g protein)
- 12oz sweet potato (75g carbs)
- Mixed vegetables
- Total: ~60g protein, 650 calories
Cutting Meal Examples
Meal 1: High-Protein Breakfast
- 6 egg whites + 2 whole eggs (32g protein)
- 1 cup oats (5g protein)
- Berries
- Total: ~37g protein, 400 calories
Meal 2: Lean Lunch
- 8oz chicken breast (62g protein)
- 1 cup rice (45g carbs)
- Large vegetables serving
- Total: ~62g protein, 450 calories
Meal 3: Protein-Focused Dinner
- 8oz white fish or chicken (50-60g protein)
- Large salad
- 1/2 avocado (healthy fats)
- Total: ~55g protein, 400 calories

The Bottom Line: Variety and Consistency Beat Perfection
After examining all 20 foods:
The truth about muscle-building foods:
✅ No single food is mandatory (build diet with foods you enjoy and can afford)
✅ Protein quality matters most (complete amino acids, high biological value)
✅ Cost-effectiveness is crucial (long-term muscle building requires affordable nutrition)
✅ Variety prevents boredom (rotating foods supports adherence)
✅ Practical foods win (easiest to prepare and eat consistently are best)
The core foods to prioritize:
Protein sources (choose 3-5):
- Eggs (most versatile)
- Chicken breast (best value)
- Greek yogurt (convenient)
- Lean beef (nutrient-dense)
- Tuna (affordable, portable)
Carbohydrate sources (choose 2-4):
- Rice (white or brown, easiest)
- Oats (versatile)
- Sweet potatoes (nutrient-dense)
- Bananas (portable)
Healthy fats (choose 2-3):
- Olive oil (cooking, calories)
- Peanut butter (calories, taste)
- Nuts (portable, nutrient-dense)
- Avocado (micronutrients)

Build your foundation on 8-12 core foods, rotate others for variety.
What matters more than food selection:
- Total daily protein (0.8-1g per pound body weight)
- Appropriate calories (surplus for muscle gain, deficit for fat loss)
- Consistency (eating the plan 90%+ of the time)
- Progressive training (food supports but doesn’t replace training)
The flexible approach:
Don’t obsess over having every food on this list. Instead:
- Choose affordable options from each category
- Rotate for variety when possible
- Prioritize consistency over perfection
- Adjust to your budget and preferences
BUILD DIET ON PROVEN FOODS. PRIORITIZE CONSISTENCY. SUPPORT TRAINING WITH NUTRITION.
Ready to build a complete, personalized nutrition plan with the exact foods, portions, and timing that delivers maximum muscle growth without wasting money or overcomplicating the process? Knowing which foods build muscle is just the starting point. Get a comprehensive guide to calculating your exact calorie and macro needs, creating sustainable meal plans, timing your nutrition optimally, and building serious muscle with a science-based approach. Stop guessing about food choices. Start following a proven nutrition system.




Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.