Taking egg white protein and experiencing uncomfortable gas and bloating? Here’s why it happens and exactly how to fix it.
You started supplementing with egg white protein (albumin) to hit your protein targets. Great choice for muscle building.
But now you’re dealing with an embarrassing and uncomfortable problem: excessive gas, bloating, and flatulence.
You’re not alone. This is one of the most common complaints from egg white protein users.
The good news? This problem is usually fixable without giving up this valuable protein source entirely.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll explain exactly what egg white protein is, reveal why it causes digestive issues for many people, identify the specific culprits behind your gas and bloating, and provide proven solutions to minimize or eliminate these problems.
Whether you’re experiencing mild discomfort or severe digestive distress, this article will help you find the solution.
Let’s get into it.
What Is Egg White Protein (Albumin)?
Before we can solve the problem, you need to understand what you’re actually consuming.
The Basics
Egg white protein, often called albumin, is a protein powder made from dehydrated egg whites.
The production process:
- Egg whites are separated from yolks
- Whites are pasteurized for safety
- Water is removed through spray-drying
- Result is a fine powder that’s approximately 80-90% protein by weight
It’s essentially powdered egg whites, nothing more complex than that.
Why People Use Egg White Protein
Egg white protein offers several advantages:
Complete protein: Contains all nine essential amino acids in optimal ratios for muscle building.
High biological value: Your body can use approximately 88% of the protein you consume (similar to whey).
Lactose-free: Perfect for people with lactose intolerance who can’t use whey.
Low in carbs and fat: Nearly pure protein with minimal other macronutrients.
Cost-effective: Often cheaper than whey protein, especially for the quality you’re getting.
Slow-medium digestion: Absorbs slower than whey but faster than casein, providing sustained amino acid release.
Versatile: Can be used any time of day, unlike whey which is typically reserved for post-workout.
Nutritional Profile
Typical egg white protein powder (per 30g scoop):
- Calories: 110-120
- Protein: 24-26g
- Carbohydrates: 1-2g
- Fat: 0-0.5g
- Cholesterol: 0mg (egg whites contain no cholesterol)
- Sodium: 150-300mg (varies by brand)
Rich in:
- Leucine (critical for muscle protein synthesis)
- BCAAs (branched-chain amino acids)
- Glutamic acid
- Various other amino acids
This impressive nutritional profile makes egg white protein an excellent choice for muscle building and recovery.

So why does it cause such terrible gas for so many people?
Why Egg White Protein Causes Gas and Bloating
Let’s examine the specific reasons this protein powder creates digestive distress.
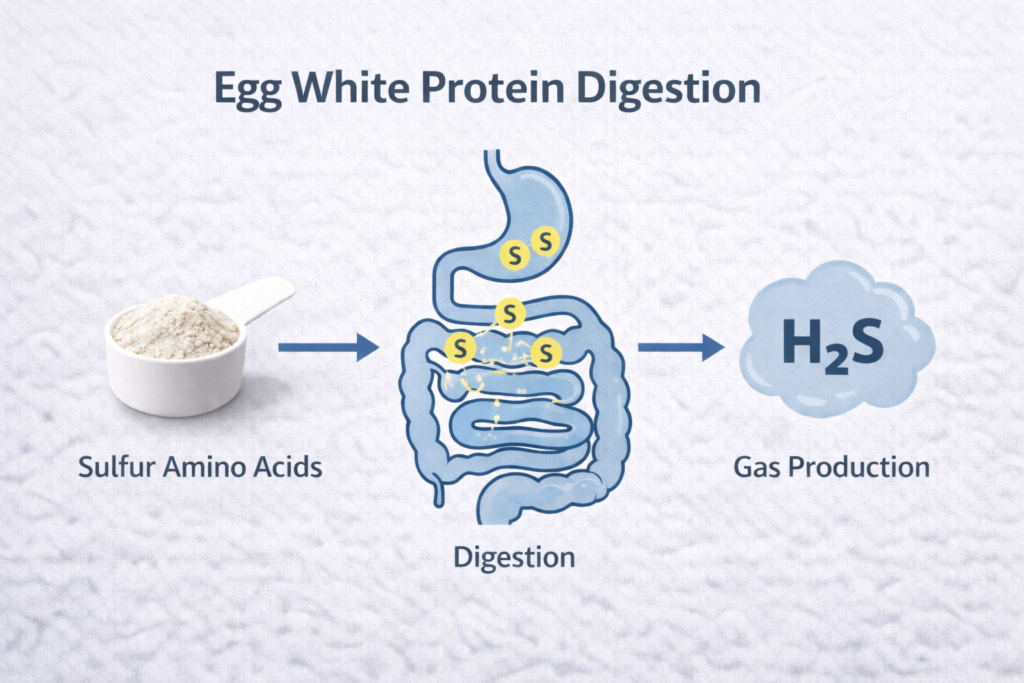
Cause 1: Sulfur-Containing Compounds
This is the primary culprit for most people.
Egg whites are naturally high in sulfur-containing amino acids:
- Methionine
- Cysteine
- Cystine
What happens:
When your digestive system breaks down these sulfur-containing proteins, it releases hydrogen sulfide gas (H₂S).
Hydrogen sulfide is the compound responsible for the characteristic “rotten egg” smell associated with flatulence from egg protein.
The more egg white protein you consume, the more sulfur compounds need to be processed, resulting in more gas production.
Why some people are affected more than others:
Gut bacteria composition: Different bacterial species in your gut process sulfur differently. Some people’s gut microbiome produces more H₂S than others.
Digestive enzyme levels: Variations in how efficiently you digest protein affect sulfur breakdown.
Individual sensitivity: Some people are simply more sensitive to sulfur compounds.
Cause 2: Avidin (And Its Digestive Challenges)
Avidin is a protein found in egg whites that can cause digestive issues.
What avidin does:
Avidin binds strongly to biotin (vitamin B7), making both the avidin and biotin harder to digest.
While cooking denatures avidin (making it harmless), egg white protein powder is made from raw egg whites. Some avidin remains active in the final product.
How this causes gas:
Undigested avidin can ferment in your intestines, producing gas. Additionally, avidin’s binding properties can interfere with normal digestive processes.
Important note: The avidin content in egg white protein is relatively low and usually not problematic for most people. It’s a contributing factor, not the main cause.
Cause 3: Slow Digestion and Intestinal Fermentation
Egg white protein digests more slowly than whey protein.
Why this matters:
Longer intestinal transit time means more opportunity for fermentation to occur, especially if:
- You consume large amounts at once
- Your digestive system is already compromised
- You have an imbalanced gut microbiome
When protein sits in your intestines longer, gut bacteria have more time to ferment it, producing gas as a byproduct.
This is why some people experience worse gas several hours after consuming egg white protein rather than immediately.
Cause 4: Egg White Allergy or Sensitivity
Distinct from lactose intolerance, egg white allergy is an immune response to proteins in egg whites.
The allergenic proteins in egg whites:
- Ovalbumin (most common allergen)
- Ovomucoid
- Ovotransferrin
- Lysozyme
Symptoms of egg white allergy:
Gastrointestinal:
- Gas and bloating
- Stomach cramps
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
Other symptoms:
- Skin reactions (hives, eczema)
- Respiratory issues (in severe cases)
- Itching in mouth or throat
Important distinction:
True allergy involves immune response. Sensitivity or intolerance involves digestive difficulty without immune involvement.
If you suspect allergy rather than just digestive issues, consult an allergist for testing.
Cause 5: Lactose Contamination (Protein Blends)
Here’s something many people don’t realize:
Some “egg white protein” products are actually blends containing whey protein or other dairy proteins.
Why manufacturers do this:
- Improves mixability
- Enhances flavor
- Reduces cost
- Creates better texture
The problem: If you’re lactose intolerant and unknowingly consuming a blend with dairy, you’ll experience:
- Gas and bloating
- Diarrhea
- Stomach cramps
- Flatulence
Combined with egg white protein’s natural gas-producing tendency, this creates a perfect storm of digestive distress.
Solution: Always check the ingredient list carefully. Pure egg white protein should list only egg whites (albumin) plus possibly flavoring and sweeteners.
Cause 6: Artificial Sweeteners and Additives
Many flavored egg white protein powders contain sweeteners and additives that cause gas.
Common culprits:
Sugar alcohols:
- Sorbitol
- Xylitol
- Maltitol
- Erythritol
These are poorly absorbed in the small intestine and ferment in the large intestine, producing significant gas.
Artificial sweeteners:
- Sucralose
- Aspartame
- Acesulfame potassium
While these don’t cause gas for everyone, some people experience digestive issues from artificial sweeteners.
Thickeners and fillers:
- Inulin (fiber that can cause gas)
- Xanthan gum
- Guar gum
- Carrageenan
These can cause digestive discomfort in sensitive individuals.
Cause 7: Poor Mixing and Clumping
Egg white protein is notoriously difficult to mix smoothly.
It tends to:
- Clump easily
- Form foam on top
- Not dissolve completely
- Create a chalky texture
Why this causes gas:
Clumps of undissolved protein pass through your stomach and into your intestines partially intact.
Your digestive system struggles to break down these protein clumps efficiently, leading to:
- Incomplete digestion
- Bacterial fermentation
- Excessive gas production
- Bloating
The better mixed your shake, the easier digestion and less gas.
Cause 8: Consuming Too Much Too Quickly
Overwhelming your digestive system with excessive protein causes problems.
What happens when you consume large amounts:
Your digestive enzymes become insufficient to break down all the protein efficiently.
Undigested protein reaches your large intestine where bacteria ferment it, producing gas.
This is why consuming 50-60g of egg white protein in a single shake often causes worse gas than consuming 25g.
How to Stop the Gas and Bloating: Proven Solutions
Now let’s fix the problem with practical, effective strategies.
Solution 1: Use Pure, Unflavored Egg White Protein
This eliminates many potential gas-causing additives.
Benefits of unflavored egg white protein:
- No artificial sweeteners (no sugar alcohol fermentation)
- No unnecessary flavoring chemicals
- Fewer total ingredients to react to
- Often cheaper than flavored versions
Drawback: Taste is bland or slightly “eggy.”
How to make it palatable:
- Mix with flavored beverages (chocolate milk, flavored almond milk)
- Add to smoothies with fruit
- Blend with cocoa powder and stevia
- Use in recipes (pancakes, baked goods)
If you must use flavored protein:
- Choose naturally flavored options
- Avoid products with sugar alcohols
- Check for minimal ingredient lists
- Look for stevia-sweetened versions (usually better tolerated)
Solution 2: Reduce Number of Shakes and Serving Size
Less egg white protein means less gas production.
Strategic reduction:
Instead of: 2-3 shakes daily at 50g protein each
Try: 1-2 shakes daily at 25-30g protein each
Fill remaining protein needs with:
- Whole food sources (chicken, fish, lean beef)
- Other protein powders you tolerate better (whey isolate, plant proteins)
- Combination approach
Why this works:
Reducing the load gives your digestive system a better chance to process what you do consume.
Even if egg white protein is your preferred source, using it strategically rather than exclusively often eliminates gas issues.
Solution 3: Mix Your Shake Properly
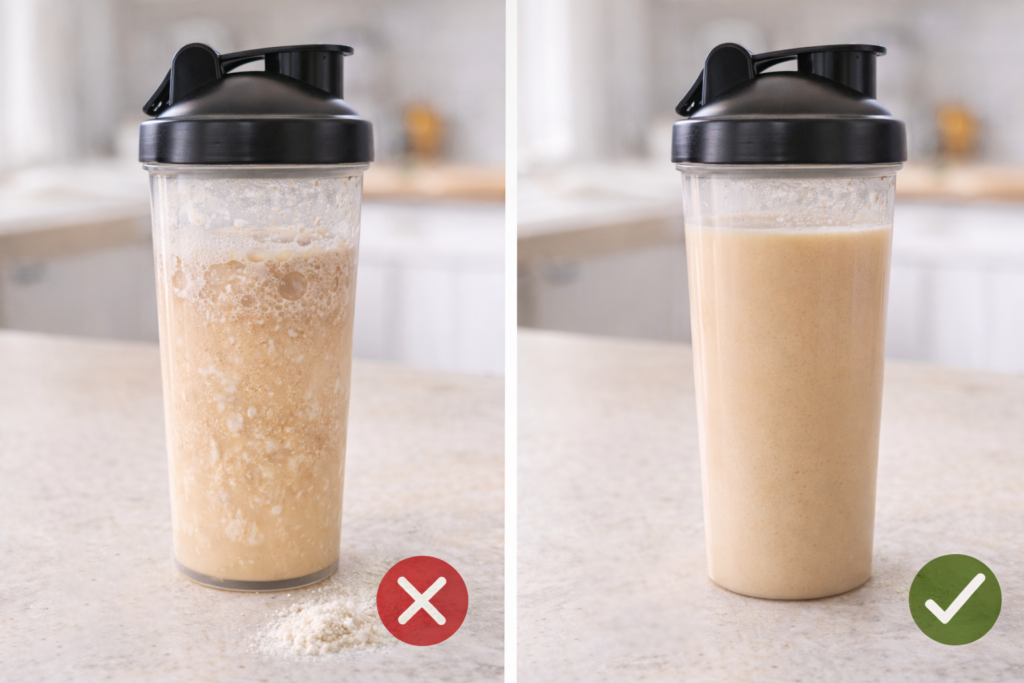

Proper mixing is critical for reducing digestive issues.
Best mixing methods:
Blender (best option):
- Add liquid first
- Add protein powder
- Blend on high for 30-60 seconds
- Creates smoothest consistency
- Minimizes clumping
Shaker bottle with mixing ball:
- Add liquid first (very important)
- Add protein powder
- Shake vigorously for 30-60 seconds
- Let sit 30 seconds, shake again
- Metal mixing ball helps break up clumps
What NOT to do:
- Don’t add protein first, then liquid (guarantees clumping)
- Don’t shake half-heartedly (won’t mix properly)
- Don’t use just a spoon in a glass (terrible mixing)
Pro tip: Let the mixed shake sit for 2-3 minutes, then shake or blend again. This gives protein time to hydrate and any remaining clumps will break up more easily.
Solution 4: Increase Water Intake Throughout the Day
Proper hydration significantly improves protein digestion.
Why water helps:
Aids digestion: Water is necessary for digestive enzymes to work efficiently.
Prevents constipation: Better digestive flow means less fermentation and gas buildup.
Dilutes gas-producing compounds: More water means less concentrated fermentation.
Supports gut health: Hydration maintains healthy intestinal lining.
How much water:
- Minimum: 8-10 glasses (64-80oz) daily
- More if training intensely
- More in hot weather
- More if consuming high protein intake
Strategic timing:
- Drink water with your protein shake
- Drink water between meals
- Stay consistently hydrated throughout the day
Solution 5: Avoid Other Gas-Producing Foods
Reduce total fermentation load by limiting other culprits.
Foods to minimize when using egg white protein:
High-fiber foods (temporarily):
- Beans and legumes
- Broccoli, cauliflower, Brussels sprouts
- Cabbage
- Onions and garlic
- Whole grains (in excess)
Carbonated beverages:
- Soda
- Sparkling water
- Beer
High-FODMAP foods:
- Wheat products
- Dairy (if lactose intolerant)
- Apples, pears
- Artificial sweeteners
Why this helps:
If your digestive system is already struggling with egg white protein, adding more fermentable substances makes it worse.
Temporarily reducing other gas-producing foods allows your system to handle the egg white protein more effectively.
Once your system adapts, you can gradually reintroduce these foods.
Solution 6: Take Digestive Enzymes
Supplementing with digestive enzymes can dramatically reduce gas.
Relevant enzymes for protein digestion:
Protease: Breaks down protein into amino acids (the most important for egg white protein)
Papain: Derived from papaya, helps digest protein
Bromelain: From pineapple, aids protein digestion
Peptidase: Further breaks down protein fragments
How to use:
- Take 1-2 capsules with your egg white protein shake
- Follow product instructions
- Quality matters (choose reputable brands)
Look for comprehensive digestive enzyme blends that include protease and other enzymes.
Popular brands:
- NOW Foods Digestive Enzymes
- Source Naturals Essential Enzymes
- Garden of Life enzymes
- Any quality blend with adequate protease
Expected results:
- Reduced gas and bloating
- Better protein digestion
- Less digestive discomfort
- Improved nutrient absorption
Solution 7: Use Probiotics to Balance Gut Bacteria

Optimizing your gut microbiome can significantly reduce gas.
How probiotics help:
Balance gut bacteria: Reduces populations of gas-producing bacteria.
Improve digestion: Beneficial bacteria aid protein breakdown.
Reduce fermentation: Better bacterial balance means less gas production.
Strengthen gut lining: Reduces overall digestive sensitivity.
Effective probiotic strains for gas reduction:
- Lactobacillus acidophilus
- Bifidobacterium lactis
- Lactobacillus plantarum
- Bifidobacterium longum
How to use probiotics:
Supplement form:
- Choose quality multi-strain probiotic
- Minimum 10 billion CFUs
- Take daily, preferably with food
- Be consistent for 4-6 weeks to see results
Fermented foods:
- Plain yogurt (if not lactose intolerant)
- Kefir
- Sauerkraut
- Kimchi
- Kombucha
Expected timeline:
- Week 1-2: Minimal change
- Week 3-4: Noticeable improvement
- Week 6+: Significant gas reduction
Important: Probiotics take time to work. Don’t expect immediate results.
Solution 8: Try Different Timing
When you consume egg white protein affects digestion.
Experiment with these timing strategies:
With meals instead of alone:
- Mix protein shake with food
- Consume during or immediately after meals
- Food aids digestion and reduces gas
Earlier in the day:
- Morning or afternoon instead of evening
- Allows more digestion time before bed
- Reduces nighttime discomfort
Spread doses throughout the day:
- Instead of 50g once, try 25g twice
- Smaller doses are easier to digest
- Reduces fermentation
Post-workout only:
- Limit egg white protein to immediately after training
- Use other proteins rest of day
- Minimal approach to identify tolerance
Solution 9: Consider Switching Protein Sources
If nothing else works, egg white protein might not be for you.
Alternative protein powders to try:
Whey protein isolate:
- Very low lactose
- Fast digesting
- Excellent amino acid profile
- Usually well-tolerated
Beef protein isolate:
- Lactose-free
- Egg-free
- Complete protein
- Less common but effective
Plant-based proteins:
- Pea protein (complete protein, well-tolerated)
- Rice protein (hypoallergenic)
- Hemp protein (omega-3s included)
- Blended plant proteins (best amino acid profile)
Hydrolyzed proteins:
- Pre-digested for easier absorption
- Usually cause fewer digestive issues
- More expensive but may be worth it
There’s no shame in finding egg white protein doesn’t work for you. The best protein powder is the one you can actually digest and use consistently.
When to See a Doctor
While gas from egg white protein is usually benign, certain symptoms warrant medical attention.
See a doctor if you experience:
Severe symptoms:
- Extreme bloating that doesn’t resolve
- Severe abdominal pain
- Bloody stools
- Persistent diarrhea or constipation
- Unintentional weight loss
Allergic reactions:
- Hives or skin reactions
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of face, lips, or throat
- Rapid heartbeat after consumption
Persistent issues despite trying all solutions:
- Gas doesn’t improve after 4-6 weeks of modifications
- Symptoms are affecting quality of life
- Unable to meet protein needs due to digestive issues
Testing your doctor might recommend:
- Allergy testing for egg whites
- Lactose intolerance test (if using blends)
- SIBO (Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth) test
- General digestive health assessment
The Bottom Line: Gas Is Fixable (Usually)
After examining all the causes and solutions:
Egg white protein causes gas primarily due to:
- Sulfur-containing amino acids
- Slower digestion allowing fermentation
- Poor mixing creating clumps
- Additives in flavored versions
- Individual sensitivity or allergy
- Excessive consumption
The good news: Most people can significantly reduce or eliminate gas by:
✅ Using pure, unflavored egg white protein
✅ Reducing serving sizes and frequency
✅ Mixing shakes properly (use a blender)
✅ Staying well-hydrated throughout the day
✅ Taking digestive enzymes with shakes
✅ Using probiotics to balance gut bacteria
✅ Timing consumption strategically
✅ Avoiding other gas-producing foods temporarily
Start with the simplest solutions first:
- Switch to unflavored egg white protein
- Reduce serving size to 25g per shake
- Mix thoroughly in a blender
- Increase water intake
If that doesn’t work, add: 5. Digestive enzymes 6. Probiotics 7. Strategic timing adjustments
If nothing works after 4-6 weeks of trying these strategies, consider switching to a different protein source.
Remember: The best protein powder is one you can actually digest and use consistently. If egg white protein causes persistent issues despite all modifications, there’s no shame in using whey isolate, plant protein, or other alternatives.
Your gut health and comfort matter more than stubbornly sticking with a protein source that doesn’t agree with you.
TRY THE SOLUTIONS. TRACK YOUR RESULTS. FIND WHAT WORKS FOR YOU.
Ready to optimize every aspect of your supplementation for maximum results without digestive distress? Egg white protein is just one option in a complete protein strategy. Get a science-based guide to choosing the right protein sources for your goals, optimizing digestion, building an effective supplement stack, and hitting your macros without uncomfortable side effects. Stop suffering. Start thriving.





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.