Adding a simple spice to your diet could enhance your muscle-building and fat-loss results? Here’s the science-backed truth about cinnamon for bodybuilding.
You’re doing everything right.
Training hard. Eating clean. Tracking macros. Getting adequate sleep.
But what if a common kitchen spice could give you an extra edge?
It sounds too simple. Too good to be true. A sprinkle of cinnamon improving your physique?
Here’s the truth: Using 1-6 grams of cinnamon daily can support muscle growth and fat loss through improved insulin sensitivity, enhanced nutrient partitioning, increased satiety, and reduced inflammation. However, the type of cinnamon matters critically: Ceylon cinnamon is safe for daily use, while Cassia cinnamon contains liver-toxic compounds and should be avoided for regular supplementation.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll explain exactly how cinnamon supports muscle building and fat loss, reveal why most people buy the wrong (potentially dangerous) type, show you the optimal dosage and timing for maximum benefits, provide specific recipes to incorporate cinnamon into your diet, and help you avoid the serious side effects from improper use.
Whether you’re bulking, cutting, or maintaining, this article will show you how to leverage this powerful spice.
Let’s optimize your nutrition with science-backed strategies.
What Does Cinnamon Do for Muscle Building and Fat Loss?
Before adding cinnamon to your diet, you need to understand the mechanisms.
Mechanism 1: Improved Insulin Sensitivity
This is the primary benefit for physique enhancement.
How it works:
Cinnamon contains bioactive compounds (particularly cinnamaldehyde and procyanidins) that:
- Mimic insulin’s action in the body
- Enhance insulin receptor sensitivity
- Improve glucose uptake into cells
- Support better nutrient partitioning
What this means for muscle building:
Better nutrient delivery:
- Improved glucose transport into muscle cells
- Enhanced amino acid uptake
- More efficient creatine absorption
- Superior glycogen storage
Practical benefits:
- Carbs more likely to fuel muscle growth vs. fat storage
- Post-workout nutrition more effective
- Better training energy from carbohydrate meals
- Enhanced recovery
What this means for fat loss:
Improved metabolic efficiency:
- Reduced insulin resistance
- Lower baseline insulin levels
- Enhanced fat mobilization
- Better blood sugar control
Practical benefits:
- Reduced fat storage from meals
- More stable energy (no crashes)
- Decreased hunger and cravings
- Easier to maintain caloric deficit
The research:
Multiple studies demonstrate cinnamon’s insulin-sensitizing effects:
- 1-6g daily improves fasting glucose
- Enhanced insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant individuals
- Improved glycemic control
- Better lipid profiles
Important context:
Cinnamon doesn’t replace:
- Proper training stimulus
- Adequate protein intake
- Appropriate caloric balance
- Consistent effort
It enhances what you’re already doing correctly.
Mechanism 2: Thermogenic Properties
Cinnamon may slightly increase metabolic rate.
How it works:
Thermogenesis:
- Bioactive compounds stimulate heat production
- Slight increase in calorie expenditure
- Enhanced fat oxidation
- Modest metabolic boost
The reality:
Effect is small:
- Not a magic fat burner
- Maybe 20-50 additional calories burned daily
- Far less than marketed fat burners claim
- Every bit helps when cutting
Better than nothing:
- Stacks with other efforts (diet, training, other strategies)
- No side effects at proper dosing
- Sustainable long-term
- Part of comprehensive approach
Don’t expect miracles, but appreciate marginal gains.
Mechanism 3: Increased Satiety
Cinnamon can help you feel fuller and more satisfied.
How it works:
Delayed gastric emptying:
- Slows stomach emptying rate
- Food stays in stomach longer
- Prolonged fullness signals
- Reduced hunger between meals
Blood sugar stabilization:
- Prevents rapid glucose spikes
- Avoids subsequent crashes
- Stable energy = less hunger
- Reduced cravings for quick energy
Practical benefits for fat loss:
Easier caloric deficit:
- Less hunger on same calories
- Reduced urge to snack
- Better adherence to diet
- Fewer unplanned meals
Improved diet quality:
- Less reaching for quick sugar fixes
- Better decision-making when hungry
- More controlled eating
- Sustainable approach
Mechanism 4: Anti-Inflammatory Effects
Chronic inflammation sabotages body composition goals.
How inflammation hurts your progress:
Impaired recovery:
- Delayed muscle repair
- Reduced adaptation to training
- Chronic soreness and fatigue
- Suboptimal muscle growth
Metabolic dysfunction:
- Insulin resistance development
- Enhanced fat storage
- Reduced fat oxidation
- Poor nutrient partitioning
Training quality:
- Decreased performance
- Reduced work capacity
- More fatigue
- Harder to progress
How cinnamon helps:
Anti-inflammatory compounds:
- Polyphenols and flavonoids
- Reduce inflammatory markers
- Support recovery
- Enhance overall health
Benefits for physique goals:
- Better recovery between sessions
- Enhanced training quality
- Improved nutrient partitioning
- Superior body composition changes
The Reality Check
Cinnamon is NOT a magic solution.
What cinnamon won’t do:
- Build muscle by itself (training does this)
- Burn fat without caloric deficit
- Replace proper nutrition
- Compensate for poor training
- Work miracles
What cinnamon CAN do:
- Enhance insulin sensitivity (5-10% improvement possible)
- Support better nutrient partitioning
- Increase satiety slightly
- Reduce inflammation modestly
- Provide marginal gains (which add up)
The proper perspective:
Cinnamon is one small piece of:
- Proper training program (70% of results)
- Adequate protein intake (20% of results)
- Appropriate caloric balance (10% of results)
- Strategic supplementation (maybe 5% of results)
- Cinnamon: 0.5-1% marginal improvement

But when everything else is optimized, 0.5-1% matters.
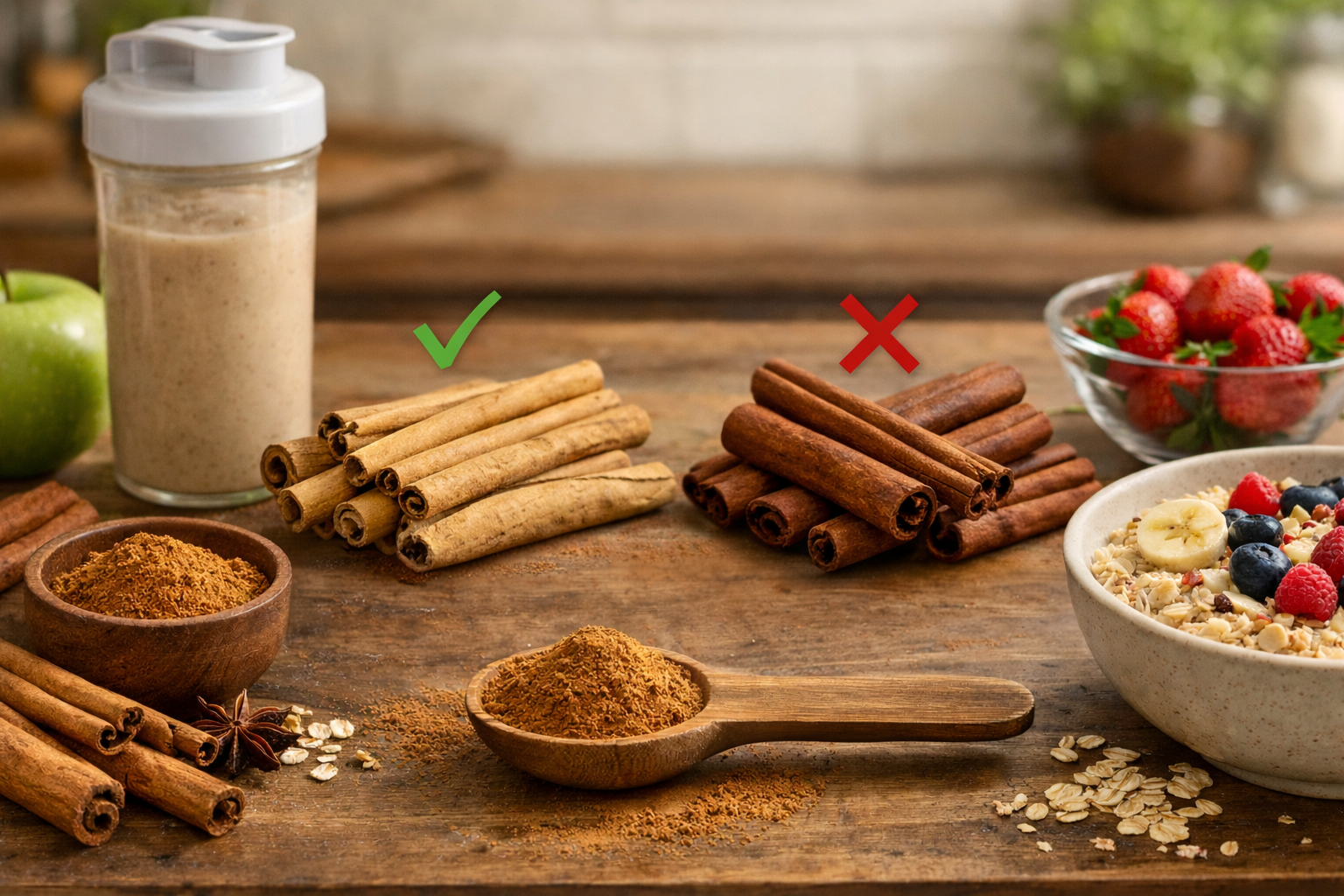
Types of Cinnamon: This Is CRITICAL (Safety Issue)
Most people buy the wrong type and risk serious health problems.
The Two Main Types
There are two commercially available cinnamon varieties:
Type 1: Cassia Cinnamon (Chinese Cinnamon)
Characteristics:
- Most common type (95%+ of supermarket cinnamon)
- Cheaper ($3-5 per container)
- Darker, reddish-brown color
- Stronger, spicier flavor
- Thicker, harder bark
The serious problem:
- Contains high levels of coumarin
- Coumarin is hepatotoxic (damages liver)
- Regular use can cause liver problems
- Unsafe for daily supplementation at effective doses
Type 2: Ceylon Cinnamon (True Cinnamon)
Characteristics:
- Less common (harder to find)
- More expensive ($10-15 per container)
- Lighter, tan-brown color
- Milder, sweeter flavor
- Thinner, more delicate bark
The critical advantage:
- Contains negligible coumarin (trace amounts)
- Safe for daily use at recommended doses
- No liver toxicity risk
- Can use long-term without concern
The Coumarin Problem Explained
Why this matters so much:
Coumarin content comparison:
- Cassia cinnamon: 0.4-0.8% coumarin by weight (extremely high)
- Ceylon cinnamon: 0.004% coumarin by weight (negligible)
- Cassia has 100-200x more coumarin than Ceylon
What happens with excess coumarin:
Short-term (weeks to months):
- Potential liver enzyme elevation
- Risk of liver inflammation
- Possible digestive issues
- Individual sensitivity varies
Long-term (months to years):
- Liver damage possible
- Hepatotoxicity documented in studies
- Risk increases with dose and duration
- Irreversible damage potential
The math that shows the problem:
If using 5g Cassia cinnamon daily:
- Coumarin intake: 20-40mg daily
- European Food Safety Authority safe limit: 0.1mg per kg body weight
- For 70kg person: Safe limit is 7mg daily
- You’re consuming 3-6x the safe limit
If using 5g Ceylon cinnamon daily:
- Coumarin intake: 0.2mg daily
- Well below safe limits
- No hepatotoxicity concern
- Safe for long-term daily use
This isn’t optional. You MUST use Ceylon cinnamon for regular supplementation.
How to Identify Ceylon Cinnamon
When buying, look for these indicators:
Label terminology:
- “Ceylon Cinnamon” (most reliable)
- “True Cinnamon”
- “Cinnamomum verum” (scientific name)
- “Sri Lankan Cinnamon”
Red flags (Cassia):
- Just “Cinnamon” without specification
- “Saigon Cinnamon”
- “Korintje Cinnamon”
- “Chinese Cinnamon”
- Very cheap price
Visual differences:
Cassia (avoid):
- Dark reddish-brown
- Thick, hard bark
- Difficult to break
- One rolled layer
Ceylon (use this):
- Light tan-brown
- Thin, delicate bark
- Brittle, easy to crumble
- Multiple thin layers rolled together
Where to buy Ceylon cinnamon:
Online (most reliable):
- Amazon (search “Ceylon Cinnamon”)
- Specialty spice retailers
- Health food stores
- Direct from reputable brands
Cost expectations:
- $10-15 for 4-8oz
- More expensive than Cassia
- Worth the safety premium
- Lasts 2-4 months at 5g daily

Don’t try to save $5-10 and risk your liver. Buy Ceylon cinnamon.
How to Use Cinnamon: Dosage, Timing, and Method
Proper usage maximizes benefits and ensures safety.
Optimal Dosage
Research-supported range: 1-6 grams daily
Dosing tiers:
Minimum effective dose: 1-2g daily
- Sufficient for some people
- Noticeable insulin sensitivity improvement
- Good starting point
- Assess individual response
Standard effective dose: 3-4g daily
- Sweet spot for most people
- Significant benefits
- Well-tolerated
- Research-backed
Maximum beneficial dose: 5-6g daily
- Upper range of studied doses
- Maximum effect
- Still safe with Ceylon cinnamon
- No additional benefit beyond 6g
Recommended approach:
Start low:
- Begin with 1-2g daily
- Assess tolerance
- Monitor effects
- Increase gradually if desired
Standard maintenance:
- 3-5g daily for most people
- Provides full benefits
- Safe long-term
- Easy to incorporate
Measurement guidelines:
1 teaspoon cinnamon ≈ 2.6g
- 1 teaspoon = ~2.6g
- 1/2 teaspoon = ~1.3g
- 2 teaspoons = ~5.2g
For precision:
- Use measuring spoons
- Or small food scale
- Track daily intake
- Stay consistent
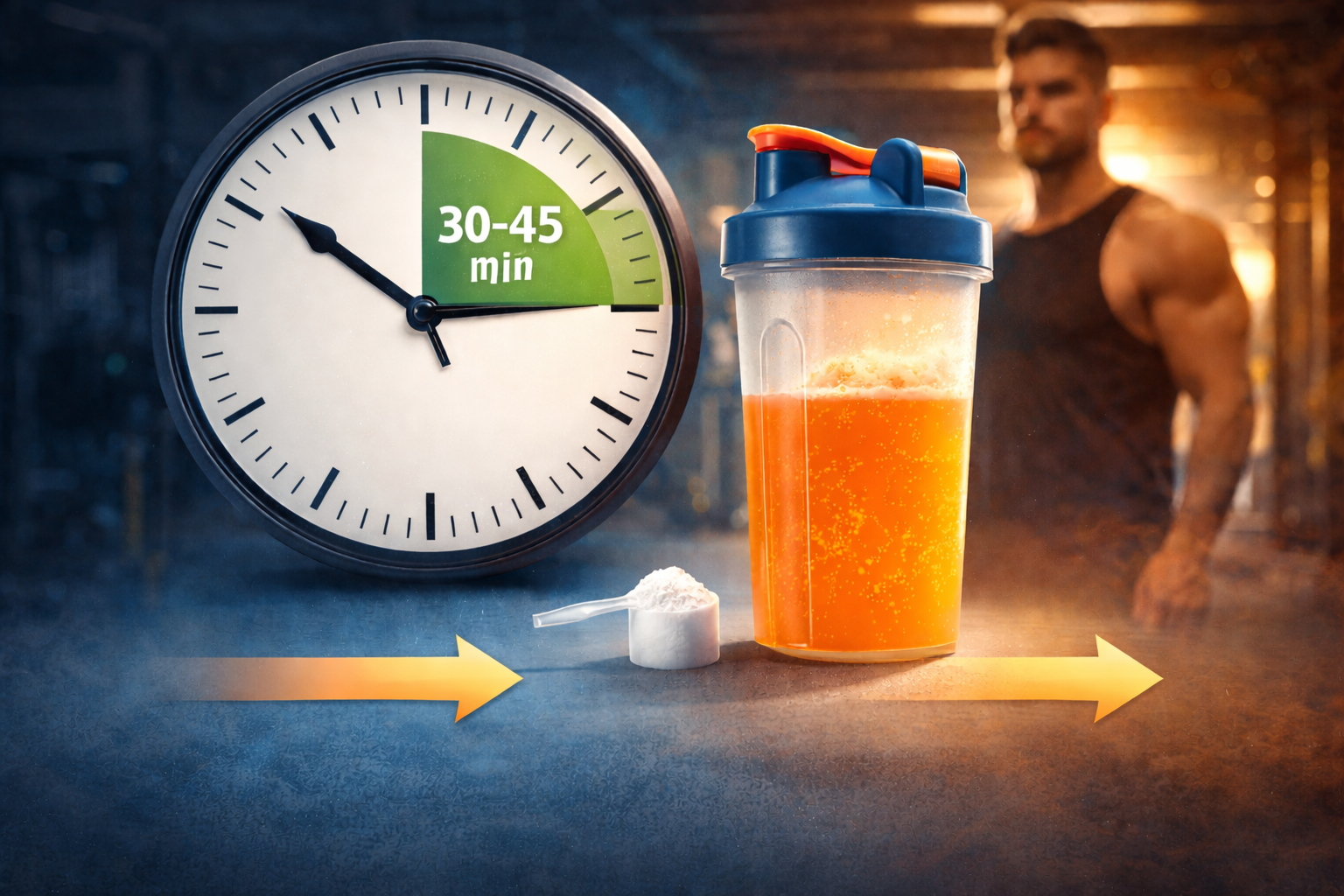
Optimal Timing
Spread intake throughout the day with meals.
Why distribute doses:
Better absorption:
- Smaller doses absorb more efficiently
- Prevents GI discomfort
- Maintains steady blood levels
- More consistent effects
Meal-based benefits:
- Improves insulin response to that meal
- Enhances nutrient partitioning when it matters
- Reduces post-meal glucose spikes
- Practical and sustainable
Example dosing schedules:
If consuming 3g daily (3 meals):
- Breakfast: 1g cinnamon
- Lunch: 1g cinnamon
- Dinner: 1g cinnamon
If consuming 5g daily (5 meals):
- Meal 1: 1g
- Meal 2: 1g
- Meal 3: 1g
- Meal 4: 1g
- Meal 5: 1g
If consuming 4g daily (4 meals):
- Breakfast: 1g
- Post-workout shake: 1g
- Lunch: 1g
- Dinner: 1g
Strategic timing (optional optimization):
Prioritize carbohydrate-heavy meals:
- Add more cinnamon to high-carb meals
- Maximizes insulin-sensitizing effects
- Enhances glucose disposal
- Better nutrient partitioning
Example:
- Breakfast (oatmeal, 80g carbs): 2g cinnamon
- Lunch (chicken salad, 20g carbs): 0.5g cinnamon
- Post-workout (rice, 100g carbs): 2g cinnamon
- Dinner (fish, vegetables, 30g carbs): 0.5g cinnamon
- Total: 5g distributed strategically
Methods of Consumption
How to actually consume 3-5g cinnamon daily:
Method 1: Mix into meals
- Oatmeal, yogurt, protein shakes
- Coffee or tea
- Baked goods
- Sauces and dressings
Method 2: Sprinkle on foods
- Fruit (apples, bananas)
- Toast or rice cakes
- Sweet potatoes
- Anything compatible
Method 3: Capsules (if preferred)
- Ceylon cinnamon capsules available
- Pre-measured doses
- Convenient
- More expensive
- Less enjoyable than food integration
CRITICAL WARNING: Never consume dry cinnamon powder directly
The “cinnamon challenge” danger:
- Dry cinnamon doesn’t dissolve with saliva
- Very fine powder
- Easy to choke or aspirate
- Can cause severe lung problems
- Potentially life-threatening

Always mix with food or liquid. Never eat dry powder.
4 High-Protein Recipes With Cinnamon
Practical ways to incorporate cinnamon into muscle-building nutrition.
Recipe 1: Protein Oatmeal Bowl
Nutrition per serving:
- Calories: 450
- Protein: 35g
- Carbs: 60g
- Fat: 10g
- Fiber: 8g
Ingredients:
- 50g rolled oats
- 30g whey protein powder (vanilla or unflavored)
- 1 medium banana, mashed
- 200ml milk (dairy or plant-based)
- 1 tablespoon (15g) peanut or almond butter
- 1-2g Ceylon cinnamon powder
- Handful chopped walnuts (20g) for topping
Instructions:
- Combine oats, milk, and cinnamon in saucepan
- Cook over medium heat, stirring constantly, until desired thickness (3-5 minutes)
- Remove from heat and add protein powder and mashed banana
- Stir vigorously to prevent clumping
- Transfer to bowl
- Top with nut butter and chopped walnuts
- Serve immediately
Best for:
- Breakfast
- Post-workout meal
- Bulking or maintenance
- Cold weather comfort food
Recipe 2: Cottage Cheese Fruit Bowl
Nutrition per serving:
- Calories: 380
- Protein: 30g
- Carbs: 50g
- Fat: 8g
- Fiber: 6g
Ingredients:
- 200g low-fat cottage cheese
- 1 banana, sliced
- 1 tablespoon (20g) honey
- 2 large whole grain rice cakes, broken into pieces
- 1-2g Ceylon cinnamon powder
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds (10g)
Instructions:
- Place cottage cheese in bowl
- Arrange banana slices on top
- Drizzle with honey
- Sprinkle cinnamon and chia seeds
- Add broken rice cake pieces for crunch
- Mix together or eat in layers
Best for:
- Snack between meals
- Pre-workout (90+ minutes before)
- Cutting (high protein, moderate calories)
- Quick, no-cook option
Recipe 3: Basic Protein Shake
Nutrition per serving:
- Calories: 520
- Protein: 40g
- Carbs: 65g
- Fat: 12g
- Fiber: 8g
Ingredients:
- 1 scoop (30g) whey protein (vanilla or chocolate)
- 1 medium frozen banana
- 40g rolled oats
- 250ml skim milk or almond milk
- 1 tablespoon (15g) peanut butter
- 1-2g Ceylon cinnamon powder
- Ice cubes as desired
Instructions:
- Add all ingredients to blender: milk, frozen banana, oats, protein powder, peanut butter, cinnamon
- Blend on high speed 60-90 seconds until completely smooth and creamy
- Add ice cubes if desired for colder, thicker consistency
- Blend additional 20-30 seconds
- Serve immediately
Best for:
- Post-workout
- Breakfast on the go
- Meal replacement
- Bulking (add more oats or PB for extra calories)
Recipe 4: Cinnamon Protein Pancakes
Nutrition per serving (3 pancakes):
- Calories: 380
- Protein: 35g
- Carbs: 45g
- Fat: 8g
- Fiber: 6g
Ingredients:
- 40g oat flour (blend oats into powder)
- 30g whey protein powder (vanilla)
- 2 large eggs
- 100ml milk
- 1 teaspoon baking powder
- 2g Ceylon cinnamon powder
- Pinch of salt
- Cooking spray
Instructions:
- Mix dry ingredients: oat flour, protein powder, baking powder, cinnamon, salt
- In separate bowl, whisk eggs and milk
- Combine wet and dry ingredients, mix until smooth (don’t overmix)
- Let batter rest 2-3 minutes (will thicken)
- Heat non-stick pan over medium heat, spray with cooking spray
- Pour 1/3 of batter into pan for each pancake
- Cook 2-3 minutes until bubbles form and edges set
- Flip and cook another 2 minutes
- Serve with sugar-free syrup, Greek yogurt, or fruit
Best for:
- Weekend breakfast
- Pre-workout meal (2-3 hours before)
- Post-workout
- Satisfies sweet cravings healthily

Side Effects, Restrictions, and Safety Precautions
Important warnings before using cinnamon therapeutically.
Who Should NOT Use Cinnamon Supplementation
Absolute contraindications:
People with liver disease:
- Even Ceylon cinnamon should be avoided
- Liver already compromised
- Cannot process compounds safely
- Risk of further damage
People with gastrointestinal ulcers or gastritis:
- Cinnamon can irritate stomach lining
- May worsen existing conditions
- Can delay healing
- Choose other strategies
People on blood-thinning medications:
- Cinnamon has anticoagulant properties
- May enhance medication effects
- Risk of excessive bleeding
- Consult doctor before use
Pregnant or breastfeeding women:
- Safety not established at supplemental doses
- Culinary amounts (food flavoring) safe
- 3-6g daily not studied in pregnancy
- Err on side of caution
People with cinnamon allergy:
- Obvious but worth stating
- Some people allergic to cinnamon
- Can cause serious reactions
- Avoid completely
Potential Side Effects Even With Ceylon Cinnamon
At recommended doses (1-6g daily), most people tolerate well, but possible issues include:
Digestive discomfort:
- Stomach irritation
- Nausea (especially on empty stomach)
- Heartburn or acid reflux
- Diarrhea (rare)
Solution:
- Take with meals (never empty stomach)
- Start with lower dose (1-2g)
- Spread throughout day
- Reduce dose if issues persist
Mouth/lip irritation:
- Cinnamon can irritate mucous membranes
- Especially with direct contact
- Rarely problematic when mixed with food
- Avoid dry powder
Allergic reactions:
- Rare but possible
- Symptoms: rash, itching, swelling
- Stop use immediately
- Seek medical attention if severe
Drug Interactions
Cinnamon may interact with certain medications:
Diabetes medications:
- Cinnamon lowers blood sugar
- Combined with diabetes meds may cause hypoglycemia
- Monitor blood sugar closely
- Adjust medication with doctor guidance
Blood thinners (warfarin, aspirin, etc.):
- Cinnamon has anticoagulant properties
- May enhance medication effects
- Increased bleeding risk
- Consult doctor before combining
Liver medications:
- Any medication processed by liver
- Potential interactions possible
- Monitor liver function
- Medical supervision recommended
If taking ANY medication regularly, consult your doctor before supplementing with cinnamon at therapeutic doses.
The Aspiration Danger (Extremely Important)
Never attempt to swallow dry cinnamon powder.
Why this is dangerous:
Cinnamon’s physical properties:
- Extremely fine powder
- Hydrophobic (repels water)
- Doesn’t dissolve in saliva
- Doesn’t clump together
What happens if you try:
- Immediate choking reflex
- Powder coats throat and mouth
- Impossible to swallow
- Gag reflex triggers
- Powder inhaled into lungs
Serious consequences:
- Aspiration pneumonia
- Lung inflammation
- Respiratory distress
- Potential hospitalization
- Documented deaths
The “cinnamon challenge”:
- Internet trend from 2010s
- People attempting to swallow tablespoon of cinnamon
- Resulted in numerous hospitalizations
- Never, ever attempt this
- Not funny, actually dangerous
Safe consumption only:
- Mixed thoroughly into food
- Dissolved in liquids
- Part of recipe
- Never dry or alone
Quality and Purity Concerns
Buy from reputable sources:
Potential contamination issues:
- Heavy metals (lead concern in some cinnamon)
- Pesticide residues
- Adulteration with cheaper substances
- Manufacturing quality varies
How to ensure quality:
- Buy certified organic when possible
- Choose reputable brands
- Look for third-party testing
- Read reviews and research brands
- Don’t buy cheapest option
Storage for freshness:
- Airtight container
- Cool, dark location
- Away from heat and moisture
- Replace every 6-12 months for potency

The Bottom Line: Ceylon Cinnamon Can Support Your Goals Modestly
After examining all the evidence:
The truth about cinnamon for muscle building and fat loss:
✅ Improves insulin sensitivity (5-15% improvement documented)
✅ Enhances nutrient partitioning (directs nutrients toward muscle vs. fat)
✅ Increases satiety modestly (helps with diet adherence)
✅ Reduces inflammation (supports recovery)
✅ Provides marginal but real benefits (0.5-1% improvement when everything else optimized)
Critical safety requirements:
❌ Never use Cassia cinnamon for daily supplementation (liver toxicity risk)
✅ Always use Ceylon cinnamon (safe for long-term use)
❌ Never consume dry powder (aspiration danger)
✅ Always mix with food or liquid (safe consumption)
The optimal usage protocol:
Dosage: 3-5g Ceylon cinnamon daily (start with 1-2g and increase)
Timing: Spread evenly across meals (1g per meal if eating 3-5 times daily)
Method: Mixed into food or beverages (oatmeal, shakes, coffee, yogurt)
Duration: Long-term use safe with Ceylon variety
What cinnamon won’t do:
- Build muscle without training
- Burn fat without caloric deficit
- Replace proper nutrition
- Work miracles
- Compensate for poor habits
What cinnamon CAN do:
- Support better insulin function (meaningful)
- Enhance nutrient use efficiency (helpful)
- Increase fullness slightly (aids diet adherence)
- Reduce chronic inflammation (supports recovery)
- Provide marginal gains that add up (when everything else optimized)
The proper perspective:
Cinnamon is one small tool in comprehensive approach. It works best when:
- Training program is solid
- Nutrition is on point
- Protein intake adequate
- Calories appropriate for goals
- Sleep and recovery prioritized
- Consistency maintained
At that point, cinnamon’s 0.5-1% contribution matters and adds up over time.
BUY CEYLON CINNAMON. USE 3-5G DAILY WITH MEALS. SUPPORT YOUR OPTIMIZED NUTRITION PLAN.
Ready to optimize every aspect of your nutrition and training for maximum muscle building and fat loss without wasting money on useless supplements or strategies? Cinnamon is one small piece of evidence-based nutrition. Get a complete guide to calculating your exact macro needs, building a whole food diet that works, timing your nutrition optimally, and using supplements and food strategies that actually deliver results. Stop hoping for magic solutions. Start using proven strategies that work.





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.