Think oxytocin is just for women? Science reveals this “bonding hormone” profoundly affects male health, relationships, performance, and well-being in ways most men never realize.
You’ve probably heard of oxytocin referred to as the “love hormone” or “cuddle hormone,” typically discussed in the context of maternal bonding and childbirth.
But here’s what most people don’t know: oxytocin plays a crucial, often overlooked role in male physiology, psychology, and performance.
This powerful hormone influences everything from your ability to build meaningful relationships to your stress levels, sexual satisfaction, cardiovascular health, and even your capacity for empathy and trust.
Yet most men remain completely unaware of how oxytocin affects their daily lives and overall well-being.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll explain exactly what oxytocin is, reveal its surprising effects on the male body and mind, show you how to naturally increase your levels, and discuss supplements that can support optimal oxytocin production.
Understanding and optimizing this hormone could transform your relationships, reduce your stress, improve your health, and enhance your quality of life.
Let’s explore the science.
What Is Oxytocin?
Oxytocin is a peptide hormone produced in the hypothalamus and secreted by the posterior pituitary gland (neurohypophysis).
The Basic Biology
Chemical structure: Nine amino acids arranged in a specific sequence (a nonapeptide)
Production site: Hypothalamus (specifically, the paraventricular and supraoptic nuclei)
Release site: Posterior pituitary gland
Target tissues: Throughout the body and brain, including receptors in the heart, blood vessels, reproductive organs, and numerous brain regions
Beyond the “Motherhood Hormone” Stereotype
While oxytocin is famous for its role in:
- Inducing uterine contractions during childbirth
- Facilitating milk ejection during breastfeeding
Its functions extend far beyond maternal physiology.
Oxytocin’s Broader Role
Beyond its reproductive functions in women, oxytocin is intimately linked to the modulation of social and emotional behaviors in both sexes, influencing aspects such as:
Empathy: The ability to understand and share the feelings of others
Bonding formation: Creating and maintaining emotional connections with partners, friends, and family
Interpersonal trust: The foundation of all meaningful relationships
Stress response: How we handle pressure and adversity
Social recognition: Remembering and recognizing people we’ve interacted with
The Scientific Evidence
Recent studies have explored oxytocin’s role in promoting prosocial behaviors and reducing stress responses.
Groundbreaking research published in Nature demonstrated that oxytocin administration can increase trust between individuals, facilitating positive social interactions.
These findings suggest that oxytocin acts as a neurochemical modulator, contributing to social cohesion and emotional well-being in both men and women.
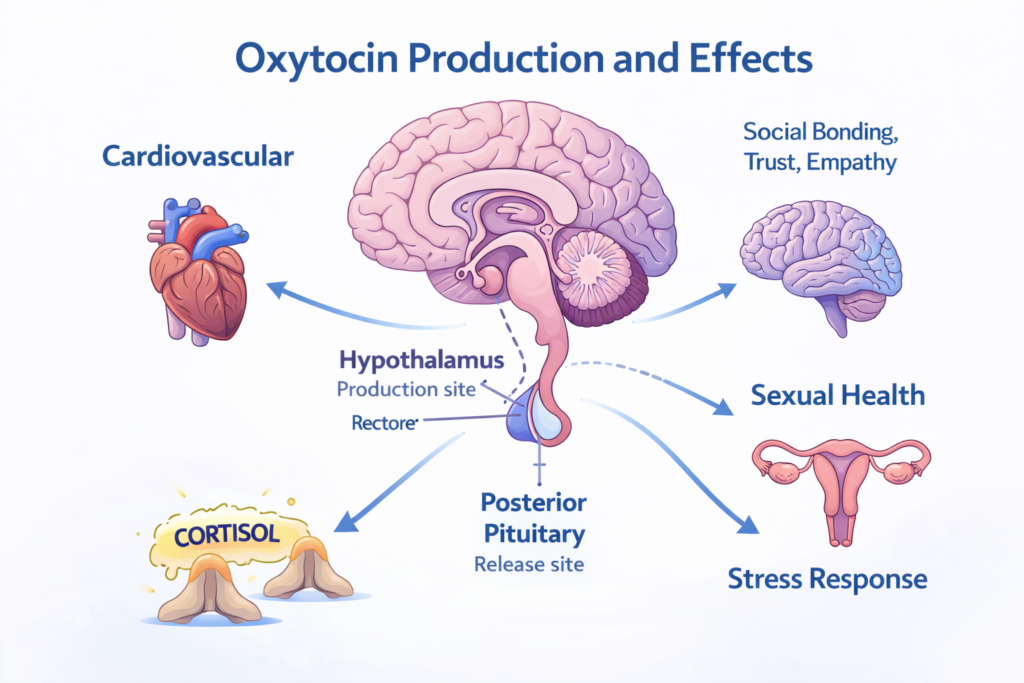
Oxytocin’s Effects on Men: Beyond What You Imagine
While oxytocin is widely recognized for promoting emotional and social bonds, its effects on men are far more extensive and nuanced than commonly understood.
Effect 1: Enhanced Emotional Connection and Bonding
In the male brain, oxytocin plays a crucial role in emotional regulation and social bonding.
How it works:
Oxytocin helps men connect more deeply with others and develop stronger bonds with romantic partners, friends, and family members.
This influence is especially evident in situations requiring:
- Empathy
- Trust
- Understanding
- Vulnerability
- Emotional openness
Practical implications:
Romantic relationships: Higher oxytocin levels correlate with greater relationship satisfaction, commitment, and emotional intimacy.
Father-child bonding: Oxytocin facilitates paternal bonding, helping fathers connect emotionally with their children. Men who engage in caregiving behaviors (holding, playing with children) show increased oxytocin levels.
Friendship quality: The hormone supports the formation and maintenance of meaningful friendships, not just romantic relationships.
Team cohesion: In group settings, oxytocin promotes cooperation, trust, and group loyalty.
Effect 2: Powerful Stress Reduction and Anxiety Management
One of oxytocin’s most valuable effects for men is its ability to reduce stress and anxiety.
The mechanism:
When oxytocin levels are elevated, there’s a corresponding decrease in cortisol production. Cortisol is the primary stress hormone, responsible for the “fight or flight” response.
By reducing cortisol, oxytocin:
- Promotes feelings of calm and well-being
- Improves overall mood
- Enhances emotional resilience
- Reduces anxiety symptoms
The science:
Research shows that oxytocin can increase a man’s capacity to face challenging situations with greater emotional balance and composure.
This makes it a powerful tool for stress management, particularly important in our high-stress modern world.
Practical benefits:
Work stress: Better ability to handle workplace pressure and interpersonal conflicts
Performance anxiety: Reduced anxiety before important events, presentations, or competitions
General anxiety: Lower baseline anxiety levels throughout daily life
Emotional regulation: Improved ability to manage emotional reactions to stressors
Effect 3: Enhanced Sexual Health and Satisfaction
Oxytocin significantly impacts male sexual health and function in multiple ways.
Sexual desire and arousal:
Oxytocin doesn’t just stimulate sexual desire; it’s intricately involved in the entire sexual response cycle.
During sexual activity:
- Enhances arousal and pleasure
- Increases sensitivity to touch
- Promotes emotional connection with partner
- Intensifies orgasm experience
The orgasm connection:
Oxytocin is released in large quantities during orgasm, creating a powerful feedback loop:
Oxytocin during sex → Enhanced pleasure → Stronger orgasm → Massive oxytocin release → Deepened emotional bond with partner
This is why sex in committed, loving relationships tends to be more satisfying than casual encounters. The oxytocin released strengthens the emotional connection, making future interactions even more rewarding.
Relationship quality impact:
Higher oxytocin levels are associated with:
- Greater sexual satisfaction
- More frequent sexual activity in committed relationships
- Stronger emotional intimacy
- Better communication about sexual needs
- Reduced likelihood of infidelity
Oxytocin can be considered an essential component for maintaining a healthy, gratifying sex life.
Effect 4: Cardiovascular Health Benefits
Beyond emotional and sexual benefits, oxytocin contributes to physical well-being, particularly cardiovascular health.
Blood pressure regulation:
Oxytocin has a hypotensive effect, meaning it can help lower blood pressure.
How it works:
- Dilates blood vessels (vasodilation)
- Reduces arterial stiffness
- Decreases cardiac workload
- Promotes overall cardiovascular relaxation
The touch connection:
When associated with affectionate behaviors like hugging, cuddling, and physical touch, oxytocin promotes a calming effect that directly benefits the cardiovascular system.
Research findings:
Studies have shown that regular physical affection and the resulting oxytocin release can:
- Lower resting blood pressure
- Reduce heart rate variability
- Improve heart rate recovery after stress
- Decrease overall cardiovascular disease risk
This relaxing effect is one reason why physical contact is so important for physiological balance.
Regular hugs, cuddles, and physical affection aren’t just emotionally satisfying; they’re literally good for your heart.
Effect 5: Improved Social Cognition and Empathy
Oxytocin enhances the ability to read social cues and understand others’ emotional states.
Social intelligence benefits:
Better facial recognition: Enhanced ability to recognize and remember faces
Emotion reading: Improved capacity to identify emotions in others through facial expressions and body language
Empathy enhancement: Greater ability to understand and share others’ feelings
Social memory: Better recall of social interactions and relationship details
Why this matters for men:
Traditionally, men are often socialized to suppress emotional expression and may struggle more with emotional intelligence than women.
Oxytocin can help bridge this gap, enhancing natural empathy and social understanding.
Effect 6: Pain Reduction and Physical Recovery
Emerging research suggests oxytocin may have analgesic (pain-relieving) properties.
How it works:
Oxytocin appears to modulate pain perception through several mechanisms:
- Reducing inflammation
- Modulating pain signal transmission
- Promoting relaxation that reduces muscle tension
- Enhancing overall pain tolerance
Practical applications:
Post-workout recovery: The oxytocin released through positive social interaction may aid muscle recovery
Chronic pain management: May help those dealing with ongoing pain conditions
Injury healing: Potential role in supporting the healing process
Effect 7: Enhanced Trust and Cooperation
One of oxytocin’s most fascinating effects is its impact on trust and cooperative behavior.
The trust study:
Research published in Nature demonstrated that intranasal oxytocin administration significantly increased trust in economic games where participants had to decide whether to trust strangers with money.
Practical implications:
Business relationships: May facilitate trust-building in professional contexts
Team performance: Enhanced cooperation and collaboration in group settings
Conflict resolution: Greater willingness to see others’ perspectives and find common ground
Leadership: Improved ability to build trust and loyalty among team members

How to Increase Oxytocin Levels in Men Naturally
The good news? You don’t need medication to boost your oxytocin levels. Several natural, accessible practices can significantly increase this beneficial hormone.

Method 1: Physical Touch and Affection
Touch is one of the most powerful stimuli for oxytocin release.
Effective forms of physical contact:
Hugging: Even brief hugs (20+ seconds) trigger oxytocin release. Make hugging friends and family a regular practice.
Kissing: Passionate kissing with a romantic partner creates a significant oxytocin surge.
Massage: Both giving and receiving massage increases oxytocin. Partners can exchange massages for mutual benefit.
Cuddling: Extended physical contact while watching TV, reading, or just relaxing promotes sustained oxytocin elevation.
Hand-holding: Simple but effective. Even holding hands while walking stimulates oxytocin production.
Sexual intimacy: Caressing, foreplay, and sexual activity are highly effective at stimulating oxytocin production.
The frequency factor:
Regular physical affection is more beneficial than occasional intense contact. Daily hugs and touch are more effective than weekly passionate encounters alone.
Method 2: Positive Social Interactions
Quality time with friends and family is another powerful oxytocin booster.
What works:
Meaningful conversations: Deep, authentic discussions (not small talk) trigger oxytocin release.
Shared laughter: Laughing together creates bonding and releases oxytocin.
Emotional support: Both giving and receiving support increases the hormone.
Collaborative activities: Working together toward a common goal promotes oxytocin production.
Shared meals: Eating together in a relaxed, social setting enhances bonding and oxytocin release.
Quality over quantity:
One deep, meaningful interaction is more valuable than multiple superficial ones. Focus on authentic connection, not just social quantity.
Method 3: Mindfulness and Meditation Practices
Meditation and relaxation activities can contribute to increased oxytocin levels.
Effective practices:
Mindfulness meditation: 10-20 minutes of focused awareness meditation can increase oxytocin while reducing cortisol.
Loving-kindness meditation: Specifically focusing on compassion and goodwill toward others is particularly effective for oxytocin release.
Yoga: Combines physical movement, breathing, and mindfulness for comprehensive stress reduction and oxytocin enhancement.
Deep breathing exercises: Slow, controlled breathing activates the parasympathetic nervous system and supports oxytocin production.
How it works:
These practices reduce stress and increase present-moment focus, creating an optimal environment for beneficial hormone production, including oxytocin.
Method 4: Acts of Kindness and Generosity
Doing something good for another person is a powerful stimulus for oxytocin release.
Examples:
Volunteering: Regular volunteer work creates sustained increases in oxytocin.
Random acts of kindness: Paying for a stranger’s coffee, helping someone carry groceries, or other spontaneous generous acts.
Charitable giving: Donating money or resources to important causes.
Helping friends: Going out of your way to assist people you care about.
Mentoring: Sharing knowledge and guiding others in their development.
The paradox of giving:
These gestures benefit the recipient, but they also provide a profound sense of happiness and connection for the giver. It’s a win-win for oxytocin production.
Method 5: Pet Interaction
Interacting with animals, particularly dogs, significantly increases oxytocin in both the human and the animal.
What the research shows:
Studies demonstrate that petting a dog, making eye contact with your pet, or playing with animals creates mutual oxytocin release.
Benefits:
Stress reduction: Immediate calming effect from animal interaction
Companionship: Reduced loneliness and isolation
Unconditional positive regard: Pets provide non-judgmental affection that triggers oxytocin
For those without pets: Consider volunteering at animal shelters, spending time with friends’ pets, or visiting pet cafes.
Method 6: Music and Singing
Listening to music, especially singing in groups, can increase oxytocin levels.
Particularly effective:
Group singing: Choirs, group singing sessions, or even singing with friends triggers significant oxytocin release.
Playing music with others: Bands, orchestras, or informal jam sessions create bonding and oxytocin.
Dancing: Particularly partner dancing or group dancing that involves coordination and touch.
Method 7: Warm Temperature Exposure
Interestingly, warmth appears to promote oxytocin release.
Practical applications:
Warm baths: Soaking in a warm bath before bed promotes relaxation and oxytocin.
Sauna sessions: Regular sauna use may support oxytocin production while providing numerous other health benefits.
Warm beverages: The ritual and warmth of tea or coffee can trigger mild oxytocin responses.
Supplements That Support Oxytocin Production
While oxytocin itself is not commonly available as a supplement (and would require injection to be effective), several supplements can stimulate its natural production.

Supplement 1: Magnesium
What it is: An essential mineral involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body.
How it helps oxytocin:
Magnesium plays an important role in neurological health and hormonal regulation. Research shows it can help promote oxytocin release, especially during relaxation and physical contact situations.
Dosage: 200-400mg daily, preferably magnesium glycinate or magnesium threonate for better absorption and neurological benefits.
Additional benefits:
- Improved sleep quality
- Reduced muscle tension
- Better stress management
- Enhanced exercise recovery
Supplement 2: Vitamin D
What it is: A fat-soluble vitamin that functions more like a hormone in the body.
How it helps oxytocin:
Vitamin D is related to the release of various hormones, including oxytocin. Adequate vitamin D levels are fundamental for optimal hormonal function.
How to get it:
Sun exposure: 15-30 minutes of midday sun exposure on significant skin surface area (arms, legs, back) is the most natural source.
Supplementation: For those without sufficient sun exposure, 2,000-5,000 IU daily is typical.
Food sources: Fatty fish, egg yolks, fortified dairy products (though amounts are relatively small).
Important note: Get blood levels tested to determine optimal dosing. Target range is typically 40-60 ng/mL.
Supplement 3: Folate (Vitamin B9)
What it is: A B-vitamin essential for DNA synthesis and neurological function.
How it helps oxytocin:
Folate plays a role in neurological health and neurotransmitter synthesis, which can indirectly increase oxytocin production.
Dosage: 400-800 mcg daily. Look for methylfolate (5-MTHF) for better absorption, especially if you have MTHFR genetic variations.
When it’s particularly useful: If there’s a deficiency impacting hormonal production.
Additional benefits:
- Improved mood
- Better cognitive function
- Enhanced cardiovascular health
- Reduced homocysteine levels
Supplement 4: L-Theanine
What it is: An amino acid found naturally in green tea.
How it helps oxytocin:
L-theanine is known for its relaxing effects without causing drowsiness. By reducing stress and promoting a sense of well-being, it can indirectly stimulate oxytocin release.
The mechanism: Reduced stress is a facilitating factor for oxytocin production. L-theanine promotes alpha brain wave activity, associated with relaxed alertness.
Dosage: 100-200mg, 1-3 times daily. Can be taken with or without caffeine (though the combination is popular for focused calm).
Additional benefits:
- Reduced anxiety without sedation
- Improved focus and attention
- Better sleep quality
- Enhanced immune function
Supplement 5: Omega-3 Fatty Acids
What they are: Essential fatty acids (EPA and DHA) found primarily in fish oil.
How they help oxytocin:
Omega-3s are renowned for their brain health and neurological benefits. They help regulate neurotransmitters and promote a state of well-being, which can stimulate oxytocin production.
Dosage: 1,000-3,000mg combined EPA+DHA daily. Look for high-quality, third-party tested fish oil to avoid mercury and contaminants.
Food sources: Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines, herring), though supplementation is often more practical for therapeutic doses.
Additional benefits:
- Reduced inflammation
- Improved cardiovascular health
- Better mood regulation
- Enhanced cognitive function
- Supported testosterone production
Supplement 6: Probiotics
What they are: Beneficial bacteria that support gut health.
How they help oxytocin:
The gut-brain axis is a bidirectional communication system. Emerging research suggests that gut health influences oxytocin production through this connection.
Specific strains: Lactobacillus reuteri has shown particular promise in animal studies for increasing oxytocin levels.
Dosage: Varies by product; look for multi-strain formulas with at least 10-50 billion CFUs, including L. reuteri if possible.
Additional benefits:
- Improved digestion
- Enhanced immune function
- Better mood (gut-brain connection)
- Reduced inflammation
Supplement 7: Vitamin C
What it is: A water-soluble antioxidant vitamin.
How it helps oxytocin:
Vitamin C is involved in the synthesis of various hormones and neurotransmitters. Adequate levels support overall hormonal health, including oxytocin production.
Dosage: 500-2,000mg daily, divided into multiple doses for better absorption.
Additional benefits:
- Powerful antioxidant protection
- Enhanced immune function
- Improved skin health
- Better iron absorption
- Supported adrenal function
Lifestyle Factors That Influence Oxytocin
Beyond specific methods and supplements, overall lifestyle significantly impacts oxytocin levels.
Sleep Quality
Poor sleep suppresses oxytocin production. Aim for 7-9 hours of quality sleep nightly.
Tips:
- Consistent sleep schedule
- Dark, cool bedroom
- Avoid screens 1-2 hours before bed
- Consider magnesium before bed
Stress Management
Chronic stress elevates cortisol, which antagonizes oxytocin. Managing stress is crucial for optimal oxytocin levels.
Effective strategies:
- Regular exercise
- Meditation or mindfulness practice
- Time in nature
- Adequate sleep
- Social connection
Alcohol Consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with oxytocin production and receptor sensitivity. Moderate your intake for optimal hormonal health.
Exercise
Regular physical activity supports overall hormonal balance, including oxytocin. However, excessive exercise without adequate recovery can suppress it.
Optimal approach: 3-5 days of moderate to intense exercise weekly with adequate rest and recovery.
The Bottom Line: Oxytocin Is Essential for Male Well-Being

Oxytocin’s effects on men are far-reaching and profound, extending well beyond simple “bonding.”
This powerful hormone influences:
✅ Emotional connection and relationship quality
✅ Stress management and anxiety reduction
✅ Sexual health and satisfaction
✅ Cardiovascular health
✅ Social cognition and empathy
✅ Pain perception and recovery
✅ Trust and cooperative behavior
The best part? You can naturally optimize your oxytocin levels through simple, accessible practices.
The action plan:
Prioritize physical affection: Regular hugs, cuddles, and physical touch with loved ones
Invest in relationships: Quality time with friends, family, and romantic partners
Practice mindfulness: Regular meditation or yoga
Be generous: Acts of kindness and helping others
Consider strategic supplementation: Magnesium, vitamin D, omega-3s, and others as needed
Manage stress: Sleep well, exercise regularly, and practice stress-reduction techniques
Optimizing oxytocin isn’t just about feeling good (though that’s a significant benefit). It’s about enhancing every aspect of your life, from your relationships to your physical health, from your stress resilience to your capacity for joy and connection.
In our increasingly isolated, high-stress modern world, oxytocin might be more important than ever.
Take action today. Hug someone you care about. Schedule quality time with friends. Start a meditation practice. Consider the supplements that might help.
Your relationships, your health, and your overall well-being will thank you.
EMBRACE CONNECTION. OPTIMIZE OXYTOCIN. TRANSFORM YOUR LIFE.
Ready to optimize every aspect of your hormonal health for peak performance, better relationships, and enhanced well-being? Oxytocin is just one piece of the puzzle. Get a complete, science-based approach to naturally optimizing testosterone, managing cortisol, and supporting overall endocrine health. Build the body, mind, and life you deserve.





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.