Want to make your whey protein shakes more effective and delicious? Here’s the complete guide to mixing whey protein for better taste, nutrition, and muscle-building results.
You bought quality whey protein. You’re committed to hitting your protein targets.
Then you open the container and wonder: What should I actually mix this with?
You’ve probably heard different advice:
- “Just use water!”
- “Always use milk for better gains!”
- “Add oats and peanut butter for mass building!”
- “Fruit juice ruins protein absorption!”
So what’s actually the best choice?
Here’s the truth that will simplify your life: You can mix whey protein with virtually any liquid or food without harming absorption. The best option depends on your specific goals (cutting, bulking, or maintenance), taste preferences, and convenience needs. Water works perfectly fine, but adding other ingredients can enhance nutrition, improve taste, and help you hit macro targets more easily.
In this comprehensive guide, I’ll explain what whey protein actually does and why mixing matters less than you think, reveal the best liquid options for different goals, show you the most effective solid ingredients to add for complete nutrition, provide specific recipes for cutting, bulking, and maintenance, and help you customize your shakes for maximum effectiveness.
Whether you’re trying to lose fat, build muscle, or just make protein shakes less boring, this article has the answers.
Let’s build better shakes.
What Whey Protein Does (And Why Mixing Doesn’t Ruin It)
Before diving into mixing options, you need to understand one critical truth.
The Primary Function of Whey Protein
Whey protein serves one main purpose: providing high-quality, convenient protein to help you meet daily protein requirements.
What whey protein provides:
- Complete amino acid profile (all nine essential amino acids)
- High leucine content (triggers muscle protein synthesis)
- Fast absorption (amino acids available within 1-2 hours)
- Convenience (mix and drink in 2 minutes)
- Precise dosing (know exactly how much protein you’re getting)
What whey protein does NOT require:
- Specific liquids to “activate” it
- Perfect timing to the minute
- Isolation from other nutrients
- Expensive specialty mixers
The Absorption Myth
Common fear: “If I mix whey with [milk/juice/food], it will slow absorption and waste the protein!”
The reality:
Whey protein gets absorbed regardless of what you mix it with.
How protein absorption actually works:
Step 1: You consume whey protein (mixed with whatever)
Step 2: It travels to your stomach where digestion begins
Step 3: Moves to small intestine where amino acids are absorbed
Step 4: Amino acids enter bloodstream and circulate to muscles
Step 5: Muscles uptake amino acids for protein synthesis
This process works whether you mix whey with:
- Plain water
- Whole milk
- Fruit juice
- A complete meal
- Literally anything edible
Yes, mixing with certain things might slow absorption slightly:
- Milk (adds fat and casein, slower digestion)
- Fiber-rich foods (slows gastric emptying)
- Large meals (everything digests slower)
But this doesn’t “ruin” the protein or prevent muscle building.
In fact, slower absorption can be beneficial:
- Provides sustained amino acid release
- Keeps you fuller longer
- Prevents rapid blood sugar spikes
- More practical for most situations
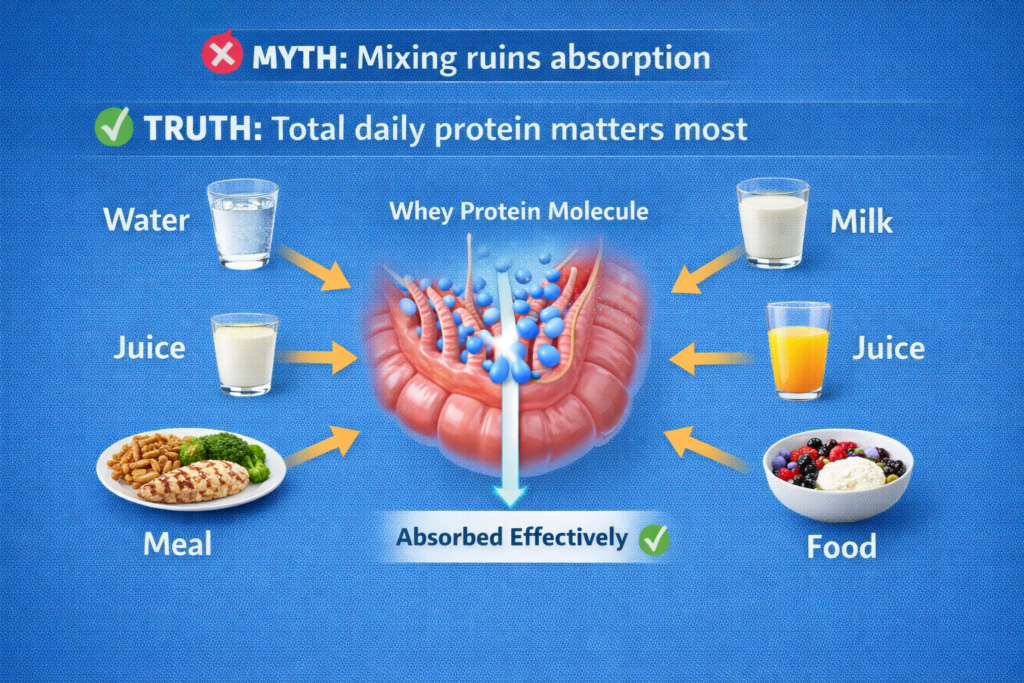
The truth: Total daily protein intake matters infinitely more than absorption speed or what you mix whey with.
Best Liquid Options for Mixing Whey Protein
Let’s examine the most common liquids and when each makes sense.
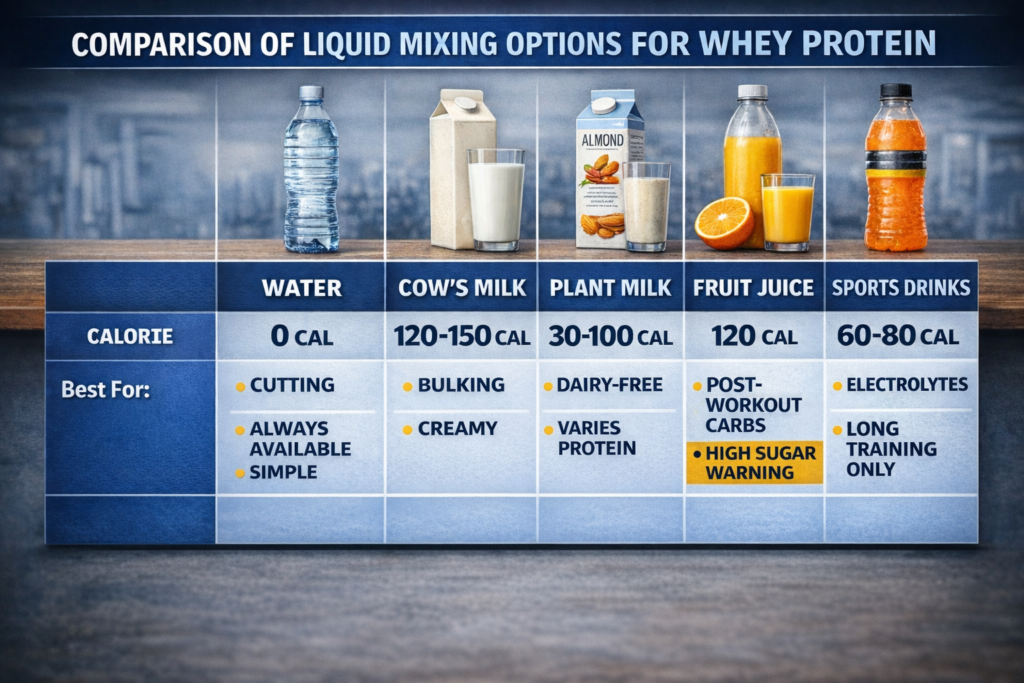
Option 1: Water (The Simple Standard)
Why water works perfectly:
Zero complications:
- No added calories
- No added macros
- No cost
- Always available
- Fast preparation
When water is the best choice:
Cutting (fat loss):
- Need to minimize calories
- Whey + water provides 120 calories and 24g protein
- Leaves maximum calories for whole food
- Helps create deficit
Post-workout:
- Fast absorption desired
- Don’t want to feel full
- Need quick protein hit
- Training again soon
On-the-go:
- Gym water fountain available
- Traveling without refrigeration
- Maximum convenience needed
- Minimal equipment required
Budget-conscious:
- Water is free
- No need to buy milk or alternatives
- Reduces supplement costs
How to make water-based shakes better:
- Use flavored whey (chocolate, vanilla, strawberry)
- Add ice for better texture
- Use shaker with mixing ball
- Drink quickly (doesn’t sit well)
Verdict: Water is always a solid choice and never a wrong choice.
Option 2: Cow’s Milk (The Creamy Upgrade)
What milk adds:
Nutritional boost:
- Additional protein (8g per cup)
- Calcium (300mg per cup)
- Vitamin D (if fortified)
- Creamier, more satisfying texture
Caloric addition:
- Whole milk: 150 calories per cup
- 2% milk: 120 calories per cup
- 1% milk: 100 calories per cup
- Skim milk: 80 calories per cup
When milk is the best choice:
Bulking:
- Need extra calories
- Want additional protein
- Creamier shake more satisfying
- Helps hit caloric surplus
Meal replacement:
- Replacing a full meal
- Need more than just protein
- Want satiety from drink
- Have 30-60 minutes to digest
Taste preference:
- Water-based shakes too thin
- Enjoy milkshake-like texture
- Want richer flavor
- Don’t mind extra calories
Considerations:
Lactose intolerance:
- Use lactose-free milk (Lactaid)
- Try whey isolate (less lactose than concentrate)
- Or switch to plant milk
Slower digestion:
- Takes 2-3 hours to fully digest
- Not ideal immediately pre-workout
- Fine for all other times
Cost:
- Milk adds $0.40-0.60 per shake
- Increases daily supplement cost
- Worth it if bulking or can afford
Verdict: Milk is excellent for bulking, meal replacement, and anyone who prefers taste over minimal calories.
Option 3: Plant-Based Milk (The Dairy-Free Alternative)
Popular options:
- Almond milk
- Oat milk
- Soy milk
- Coconut milk
- Cashew milk
- Rice milk
What plant milk provides:
Dairy-free nutrition:
- No lactose (perfect for intolerant individuals)
- Vegan-friendly
- Often fortified with calcium and vitamin D
- Lower calories than cow’s milk (usually)
Variety:
- Different flavors and textures
- Almond: Light, slightly nutty
- Oat: Creamy, naturally sweet
- Soy: Highest protein (7-9g per cup)
- Coconut: Rich, tropical flavor
When plant milk is the best choice:
Lactose intolerance:
- Can’t tolerate cow’s milk
- Want creamy texture without dairy
- Need calcium from fortified versions
Vegan diet:
- Avoiding all animal products
- Want complete plant-based shake
- Prefer ethical/environmental choice
Calorie control:
- Unsweetened almond milk: Only 30-40 calories per cup
- Much lower than cow’s milk
- Good for cutting while maintaining creaminess
Important considerations:
Protein content varies dramatically:
- Soy milk: 7-9g protein per cup (best)
- Oat milk: 2-4g protein per cup
- Almond milk: 1-2g protein per cup (minimal)
- Choose based on protein needs
Always buy unsweetened:
- Sweetened versions have 10-20g added sugar
- Unnecessary calories
- Can reach 100-150 calories per cup
- Ruins macros
Cost:
- Often more expensive than cow’s milk
- $3-5 per half gallon vs. $2-3 for cow’s milk
- Budget consideration
Verdict: Plant milk is perfect for lactose intolerance, vegan diets, and anyone preferring dairy alternatives.
Option 4: Fruit Juice (The Natural Carb Boost)
What fruit juice adds:
Natural carbohydrates:
- Quick-digesting sugars
- 25-30g carbs per cup
- Vitamins (especially vitamin C)
- Natural flavor
Energy boost:
- Fast carbs for pre or post-workout
- Replenishes glycogen quickly
- Provides immediate energy
When fruit juice makes sense:
Post-workout:
- Need fast carbs for glycogen replenishment
- Want quick protein and carb combo
- Training depleted glycogen stores
- Bulking and need easy calories
Pre-workout (90+ minutes before):
- Provides energy for training
- Easy to consume
- Won’t cause digestive issues
- Time to digest before training
Hardgainers bulking:
- Need every calorie possible
- Liquid calories easier to consume
- Don’t mind sugar from fruit
- Struggling to eat enough
Important warnings:
High sugar content:
- 20-30g sugar per cup
- Rapid blood sugar spike
- Not ideal for fat loss
- Can cause energy crash
Lacks protein and fat:
- Only provides carbs
- No satiety
- Not balanced nutrition
- Should add other ingredients
Flavor combinations matter:
- Orange juice + vanilla whey = often unpleasant
- Berry juice + chocolate whey = usually bad
- Orange juice + unflavored whey = acceptable
- Test combinations first
Better alternatives:
- Blend whole fruit instead (adds fiber)
- Use half juice, half water
- Choose 100% juice with no added sugar
- Consider this carefully vs. whole food carbs
Verdict: Fruit juice works for specific situations (post-workout, extreme bulking) but isn’t necessary for most people most of the time.
Option 5: Sports Drinks (The Electrolyte Option)
What sports drinks provide:
Electrolyte replenishment:
- Sodium (helps hydration)
- Potassium (muscle function)
- Other electrolytes
Quick carbohydrates:
- 14-20g carbs per cup
- Fast absorption
- Energy boost
When sports drinks make sense:
During/after long training:
- 90+ minute workouts
- Heavy sweating
- Need electrolyte replacement
- Combining hydration with protein
Hot weather training:
- Significant sweat loss
- Dehydration risk
- Need sodium replacement
- Convenient all-in-one solution
Athletes with high sweat rates:
- Lose significant sodium through sweat
- Cramp easily
- Benefit from electrolyte timing
- Training in heat
Considerations:
Added sugar:
- Most sports drinks have 14-20g sugar per cup
- Adds 60-80 calories
- Not ideal for cutting
- Consider sugar-free versions (Gatorade Zero, Powerade Zero)
Cost:
- More expensive than water
- $1-2 per bottle
- Adds up quickly
- Only use when actually needed
Not necessary for most:
- <60 minute workouts don’t deplete electrolytes significantly
- Regular diet provides adequate electrolytes
- Water is sufficient for most training
- Marketing overstates needs
Verdict: Sports drinks are useful for specific situations (long training, extreme heat, heavy sweaters) but unnecessary for most people most of the time.
Best Solid Ingredients to Add to Whey Protein
Now let’s explore non-liquid additions that enhance nutrition and results.
Addition 1: Oats (The Energy Foundation)
What oats provide:
Slow-release carbohydrates:
- 27g carbs per 1/2 cup
- Sustained energy for hours
- Stable blood sugar
- No crash or spike
Fiber:
- 4g fiber per 1/2 cup
- Improves digestion
- Increases satiety significantly
- Supports gut health
Additional nutrition:
- B vitamins
- Magnesium
- Iron
- Phosphorus
How to use oats in shakes:
Raw oats:
- Add 1/2 to 1 cup directly to blender
- Blend until smooth
- Creates thicker shake
- Slightly grainy texture (blend longer for smoother)
Oat flour:
- Pre-ground oats
- Mixes smoother than whole oats
- No graininess
- Perfect texture
- Can make your own (blend oats into powder)
Instant oats:
- Easiest to blend
- Smoothest texture
- Slightly less nutritious than rolled oats
- Still effective
When to add oats:
Bulking:
- Need extra calories (150 per 1/2 cup)
- Want sustained energy
- Building complete meal replacement
- Struggling to eat enough
Pre-workout (2-3 hours before):
- Provides fuel for training
- Steady energy release
- Won’t cause stomach issues if timed right
- Supports performance
Meal replacement:
- Makes shake more filling
- Provides balanced macros
- Keeps you satisfied for hours
- Complete nutrition
Not ideal for:
- Immediately post-workout (slower digestion)
- Cutting with very limited calories
- Right before training (<90 minutes)
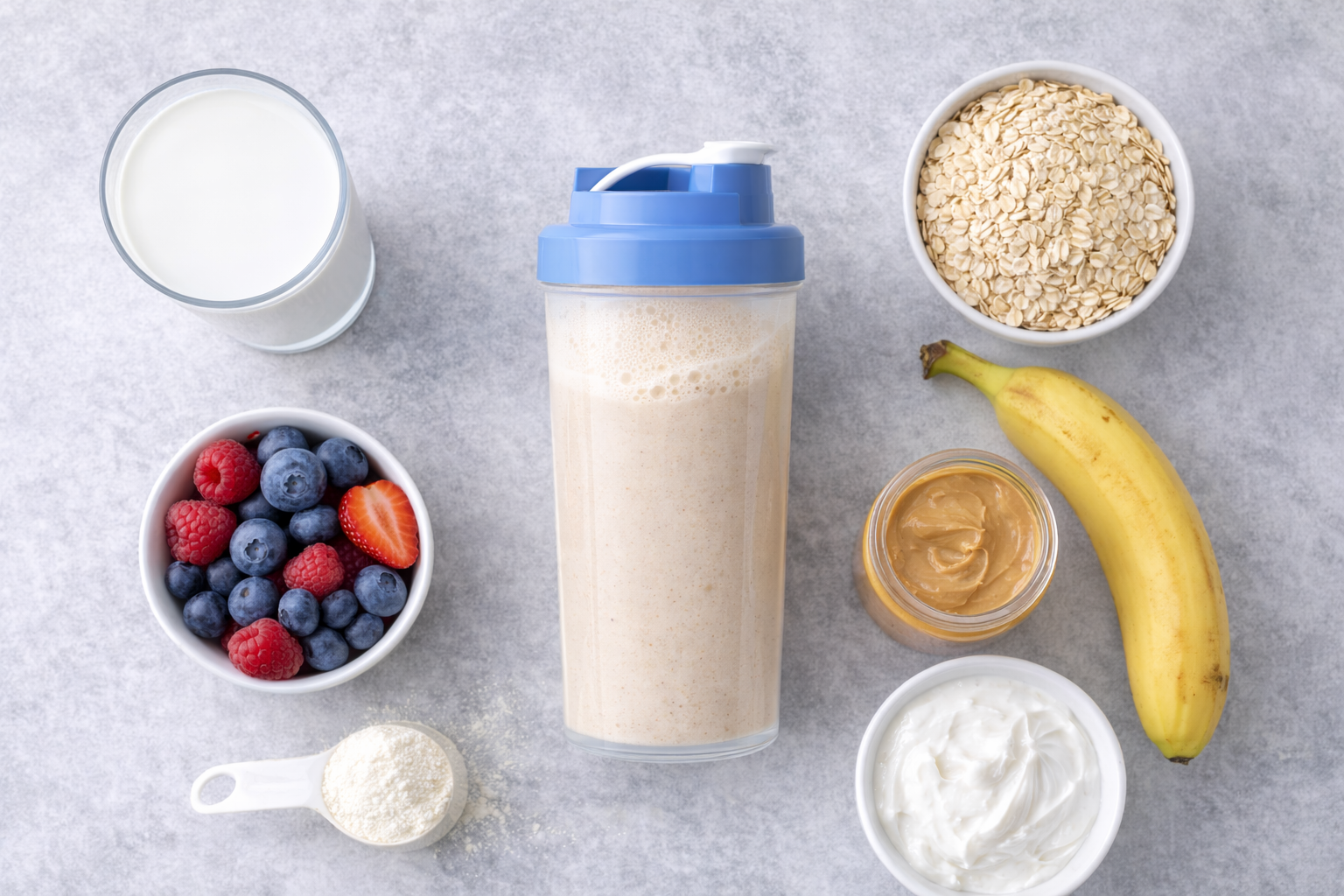
Recipe example:
- 1 scoop whey protein
- 1/2 cup oats
- 1 cup milk
- 1 banana
- Total: 520 calories, 35g protein, 75g carbs
Verdict: Oats are excellent for bulking, meal replacement, and anyone needing quality carbs with their protein.
Addition 2: Greek Yogurt (The Protein Multiplier)
What Greek yogurt adds:
Additional protein:
- 15-20g protein per cup
- Combines with whey for 35-45g total
- Slow-digesting casein protein
- Sustained amino acid release
Probiotics:
- Beneficial gut bacteria
- Improves digestion
- Supports immune function
- Enhances nutrient absorption
Creamy texture:
- Makes shake thick and satisfying
- Almost milkshake-like consistency
- Very filling
- Enjoyable to consume
Calcium:
- 200-300mg per cup
- Supports bone health
- May support fat loss
- Important for athletes
How to use Greek yogurt:
In blender:
- Add 1/2 to 1 cup
- Blend with other ingredients
- Creates thick, creamy shake
- May need more liquid to thin
As base:
- Put yogurt in bowl
- Mix in whey protein powder
- Add toppings (fruit, nuts, etc.)
- Eat with spoon like parfait
When to add Greek yogurt:
Meal replacement:
- Very filling and satisfying
- Complete nutrition
- High protein content
- Keeps you full for hours
Before bed:
- Slow-digesting casein protein
- Provides amino acids overnight
- Supports overnight recovery
- Prevents muscle breakdown
Bulking:
- Extra calories (100-150 per cup for full-fat)
- Additional protein
- Quality nutrition
- Easy to consume
Anytime satiety matters:
- Cutting and need to stay full
- Between meals
- When hunger is an issue
- Want substantial shake
Considerations:
Choose plain, unsweetened:
- Flavored yogurt has 15-25g added sugar
- Unnecessary calories
- Ruins macros
- Plain is better
Fat content options:
- Full-fat (150 cal, 8g fat): Bulking
- 2% (130 cal, 4g fat): Maintenance
- Non-fat (100 cal, 0g fat): Cutting
Lactose content:
- Contains some lactose
- May cause issues for intolerant individuals
- Try lactose-free Greek yogurt if needed
Recipe example:
- 1 scoop whey protein (24g protein)
- 1 cup plain Greek yogurt (18g protein)
- 1/2 cup berries
- Total: 300 calories, 42g protein, 30g carbs
Verdict: Greek yogurt is excellent for maximizing protein, creating filling shakes, and supporting overnight recovery.
Addition 3: Nut Butter (The Healthy Fat Source)
What nut butter provides:
Healthy fats:
- 16g fat per 2 tablespoons
- Primarily monounsaturated (heart-healthy)
- Supports hormone production
- Increases absorption of fat-soluble vitamins
Additional protein:
- 7-8g protein per 2 tablespoons
- Complements whey protein
- Plant-based protein adds variety
- Better amino acid profile combined
Calories for bulking:
- 190 calories per 2 tablespoons
- Calorie-dense and easy to add
- Doesn’t increase volume much
- Perfect for hardgainers
Delicious flavor:
- Peanut butter: Classic, versatile
- Almond butter: Slightly sweet, mild
- Cashew butter: Creamy, rich
- Any nut butter works
How to use nut butter:
Amount:
- 1-2 tablespoons typical
- Start with 1 tablespoon (95 calories)
- Add more if bulking (2-3 tablespoons)
- Easy to overdo (measure accurately)
Mixing:
- Blend for smoothest integration
- Or stir if not blending
- Natural nut butter separates (oil on top)
- Stir jar first before adding
When to add nut butter:
Bulking:
- Need extra calories easily
- Healthy fats support hormones
- Delicious and satisfying
- Makes calories easier to consume
Meal replacement:
- Provides satiety from fats
- Balanced macros (protein, carbs, fats)
- Keeps you full longer
- Complete nutrition
Pre-workout (2+ hours before):
- Sustained energy from fats
- Won’t cause stomach issues if timed properly
- Supports performance
- Prevents hunger during training
Anytime taste matters:
- Makes shakes delicious
- Chocolate whey + peanut butter = amazing
- Vanilla whey + almond butter = excellent
- Improves palatability significantly
Avoid for:
- Cutting with very limited calories (too calorie-dense)
- Immediately post-workout (slows digestion unnecessarily)
- Nut allergies (obviously)
Recipe example:
- 1 scoop chocolate whey
- 2 tablespoons peanut butter
- 1 banana
- 1 cup milk
- Total: 520 calories, 38g protein, 50g carbs, 20g fat
Verdict: Nut butter is perfect for bulking, adding healthy fats, improving taste, and creating complete meal replacements.
Addition 4: Seeds (The Nutrient Boost)
Best seeds to add:
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds (ground)
- Hemp seeds
- Pumpkin seeds
What seeds provide:
Omega-3 fatty acids:
- Anti-inflammatory
- Heart health
- Brain function
- Joint health
- Recovery support
Fiber:
- 5-10g per 2 tablespoons (depending on seed type)
- Digestive health
- Satiety
- Blood sugar stability
Protein:
- 5-6g per 2 tablespoons (hemp seeds highest)
- Plant-based protein
- Adds to total protein content
- Amino acid variety
Micronutrients:
- Magnesium (muscle function)
- Zinc (immune function, testosterone)
- Iron (oxygen transport)
- Selenium (antioxidant)
How to use seeds:
Chia seeds:
- 1-2 tablespoons
- Absorb liquid and create gel
- Makes shake thicker
- Can make it too thick if using too much
- Add right before drinking or they’ll gel
Ground flaxseeds:
- 1-2 tablespoons
- Must be ground (whole seeds pass through undigested)
- Nutty flavor
- Mix well in shakes
Hemp seeds:
- 2-3 tablespoons
- Highest protein content of seeds
- Mild flavor
- Mix easily
When to add seeds:
Cutting:
- Fiber increases satiety
- Minimal calories (50-70 per tablespoon)
- Healthy fats support hormones
- Feel fuller longer
General health:
- Omega-3s support recovery
- Micronutrients important for athletes
- Antioxidant properties
- Overall nutrition boost
Meal replacement:
- Adds complete nutrition
- Fiber keeps you satisfied
- Healthy fats balance macros
- Superfood benefits
Recipe example:
- 1 scoop whey protein
- 1 tablespoon chia seeds
- 1 tablespoon ground flaxseeds
- 1 cup berries
- 1 cup almond milk
- Total: 320 calories, 30g protein, 35g carbs, 12g fat
Verdict: Seeds are excellent for adding omega-3s, fiber, and micronutrients without many calories.
Addition 5: Cottage Cheese (The Casein Source)
What cottage cheese provides:
Slow-digesting protein:
- 14g protein per 1/2 cup
- Mostly casein (80%)
- Sustained amino acid release
- 6-8 hour digestion time
Low fat (if choosing low-fat version):
- 1% cottage cheese: 80 calories per 1/2 cup
- 2g fat
- Keeps calories controlled
- Perfect for cutting
Calcium:
- 70mg per 1/2 cup
- Bone health
- May support fat loss
- Important for athletes
How to use cottage cheese:
Amount:
- 1/2 to 1 cup
- Adjust based on calorie needs
- More for bulking, less for cutting
Blending is essential:
- Cottage cheese is lumpy
- Must blend thoroughly for smooth texture
- Creates creamy, thick shake
- Don’t try to stir (won’t work)
When to add cottage cheese:
Before bed:
- Ideal use case
- Slow protein release overnight
- Supports overnight recovery
- Prevents muscle breakdown during sleep
- Better than whey alone for this purpose
Meal replacement:
- Very filling
- High protein content
- Low calories (if using low-fat)
- Keeps you satisfied
Cutting:
- High protein, low calorie
- Extremely satiating
- Prevents muscle loss during deficit
- Helps you feel full
Recipe example (before bed shake):
- 1 scoop casein or whey protein
- 1/2 cup low-fat cottage cheese
- 1/2 cup berries
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
- Total: 280 calories, 40g protein, 25g carbs, 4g fat

Verdict: Cottage cheese is perfect for before bed, cutting, and anyone wanting sustained protein release.
Complete Shake Recipes for Different Goals
Here are proven shake recipes for specific situations.
Recipe 1: The Cutting Shake (Low Calorie, High Protein)
Goal: Maximum protein, minimal calories, high satiety
Ingredients:
- 1 scoop whey protein (vanilla or chocolate)
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
- 1/2 cup frozen berries
- 1 tablespoon ground flaxseeds
- 1/2 cup ice
- Optional: Stevia or zero-calorie sweetener
Nutrition:
- Calories: 210
- Protein: 28g
- Carbs: 18g
- Fat: 5g
- Fiber: 6g
Why this works for cutting:
- Very low calorie density
- High protein preserves muscle
- Fiber increases satiety
- Tastes great despite low calories
- Omega-3s from flax support health during deficit
Recipe 2: The Bulking Shake (High Calorie, Complete Nutrition)
Goal: Maximum calories, balanced macros, easy to consume
Ingredients:
- 2 scoops whey protein
- 1 cup whole milk
- 1 cup oats
- 2 tablespoons peanut butter
- 1 banana
- 1 tablespoon honey (optional for extra calories)
Nutrition:
- Calories: 1,020
- Protein: 62g
- Carbs: 120g
- Fat: 28g
Why this works for bulking:
- Massive calories in liquid form
- Complete macros (protein, carbs, fats)
- Quality ingredients
- Easy to consume even when full
- Tastes delicious
Recipe 3: The Post-Workout Shake (Fast Recovery)
Goal: Quick protein and carbs for optimal recovery
Ingredients:
- 1 scoop whey protein
- 1 cup low-fat milk or water
- 1 banana
- 1/2 cup frozen berries
- Optional: 1-2 tablespoons honey for extra carbs
Nutrition:
- Calories: 350
- Protein: 32g
- Carbs: 52g
- Fat: 4g
Why this works post-workout:
- Fast-digesting protein
- Quick carbs for glycogen replenishment
- Minimal fat (doesn’t slow digestion)
- Easy to consume after training
- Provides everything needed for recovery
Recipe 4: The Meal Replacement Shake (Complete Nutrition)
Goal: Replace a full meal with balanced nutrition
Ingredients:
- 1 scoop whey protein
- 1/2 cup plain Greek yogurt
- 1/2 cup oats
- 1 tablespoon almond butter
- 1 cup spinach (you won’t taste it)
- 1/2 cup berries
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
Nutrition:
- Calories: 520
- Protein: 45g
- Carbs: 55g
- Fat: 14g
- Fiber: 10g
Why this works as meal replacement:
- Complete balanced macros
- High fiber keeps you full for hours
- Greens add micronutrients
- Substantial calories
- Tastes great despite vegetables
Recipe 5: The Before Bed Shake (Overnight Recovery)
Goal: Sustained protein release during sleep
Ingredients:
- 1 scoop casein protein (or whey if no casein)
- 1/2 cup low-fat cottage cheese
- 1 tablespoon natural peanut butter
- 1 cup unsweetened almond milk
- 1/2 teaspoon cinnamon
Nutrition:
- Calories: 350
- Protein: 42g
- Carbs: 15g
- Fat: 14g
Why this works before bed:
- Slow-digesting protein (casein + cottage cheese)
- Provides amino acids for 6-8 hours
- Prevents overnight muscle breakdown
- Healthy fats support hormone production overnight
- Not too heavy or sweet

The Bottom Line: Customize Based on Your Goals
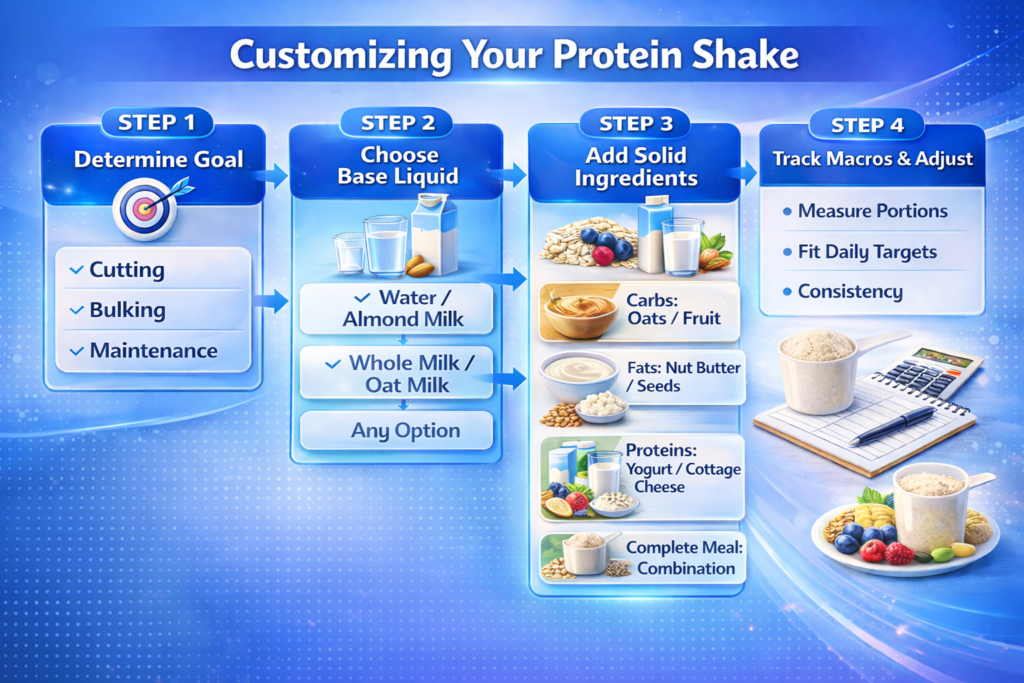
After examining all the options:
You can mix whey protein with virtually anything edible without “ruining” it.
The best liquid choices:
For cutting: Water or unsweetened almond milk (minimal calories)
For bulking: Whole milk or oat milk (extra calories and nutrition)
For convenience: Water (always available, zero cost)
For taste: Milk (any type) or plant milk (creamy and delicious)
The best solid additions:
For energy: Oats (slow-release carbs)
For protein boost: Greek yogurt or cottage cheese (extra protein)
For healthy fats: Nut butter (calorie-dense, delicious)
For nutrients: Seeds (omega-3s, fiber, micronutrients)
For complete meals: Combination of oats + nut butter + fruit + milk
The decision framework:
Step 1: Determine your goal
- Cutting: Minimize calories, maximize protein
- Bulking: Maximize calories, ensure adequate protein
- Maintenance: Balance nutrition and taste
Step 2: Choose base liquid
- Cutting: Water or unsweetened almond milk
- Bulking: Whole milk or oat milk
- Anywhere: Whatever fits your macros
Step 3: Add solid ingredients based on needs
- Need carbs: Add oats or fruit
- Need fats: Add nut butter or seeds
- Need more protein: Add Greek yogurt or cottage cheese
- Need complete meal: Add combination
Step 4: Track macros and adjust
- Ensure shake fits daily targets
- Adjust portions to match goals
- Don’t guess, measure accurately
What matters most:
- Total daily protein intake (0.7-1g per pound)
- Hitting your calorie targets for your goal
- Consistency over time
- Enjoying the process
What matters least:
- Exactly what you mix whey with
- Absorption speed differences
- Following someone else’s exact recipe
- Overthinking minor details
MIX IT WITH WHAT FITS YOUR GOALS. TRACK YOUR MACROS. STAY CONSISTENT.
Ready to optimize your entire nutrition strategy with simple, effective approaches that actually deliver results? Knowing what to mix with whey protein is just one small piece of a complete muscle-building nutrition plan. Get a comprehensive guide to calculating your exact macro needs, building a whole food diet that works, timing your nutrition optimally, and using supplements strategically for maximum results. Stop overthinking protein shakes. Start focusing on what actually matters.





Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.